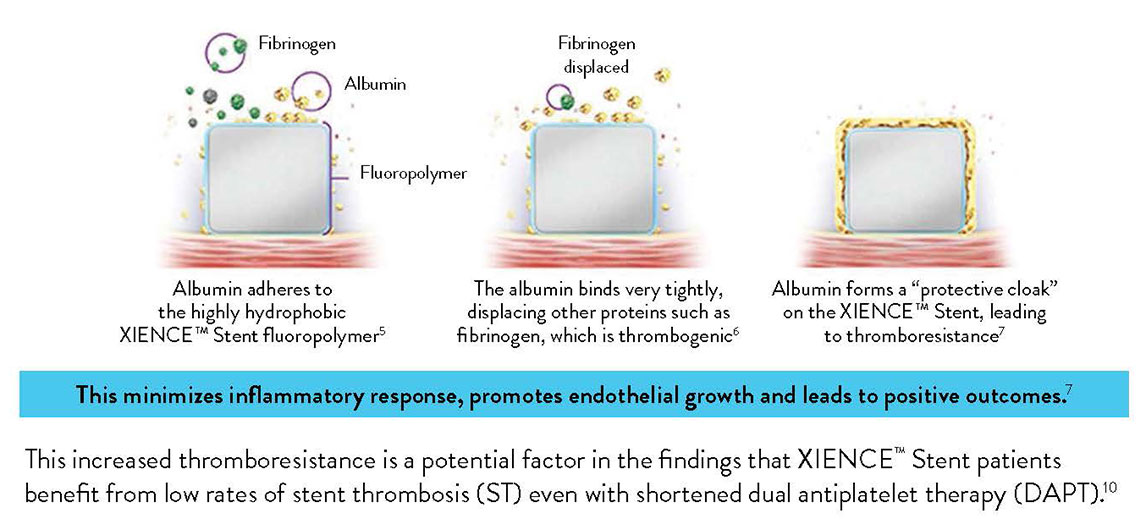
Anti-Thrombotic Fluoropolymer Promotes Safety
The XIENCE™ Stent polymer with a fluorinated surface has shown protective attributes—the ability to tightly bind albumin to create a “protective cloak” around the stent.2
The XIENCE™ Stent Fluoropolymer—Proven to Protect2,3
Another factor that sets XIENCE™ Stent apart is its fluoropolymer coating. Unlike other polymer coatings, the fluoropolymer interacts with proteins in the blood in a way that reduces thrombus formation—a process known as fluoropassivation.
Fluoropassivation Leads to Thromboresistance3
XIENCE™ Stent, widely considered to be the gold standard for patient safety and efficacy, is coated with a fluoropolymer.
THE XIENCE™ STENT FLUOROPOLYMER: PROVEN TO PROTECT
Due to thromboresistance and low inflammatory responses, fluorinated surfaces encourage faster endothelization and healing.4
Fluoropolymer Stent vs Bare Metal Stent and Biodegradable Polymer Stent
Moreover, the XIENCE™ Stent fluoropolymer has minimal coating defects compared to biodegradable polymer DES (BP-DES).9
In contrast to the visual above, most stents available today—biodegradable polymer stents, durable polymer stents or bare metal stents—have non-fluorinated surfaces that interact with proteins in the following ways:
- The surfaces attract less albumin and more fibrinogen.10
- The fibrinogen, in turn, leads to more platelet adhesion and activation.11
- The platelets, fibrinogen and red blood cells can aggregate and create a thrombus.12
XIENCE™ Stent Fluoropolymer vs Other Types of Stents
XIENCE™ Stent’s fluoropolymer demonstrates the fewest platelets adhering to the stent surface—an important factor in stent thrombosis.3 This fluoropolymer can protect patients from both acute and long-term complications.3,13
Representative confocal photomicrographs stained for platelets (CD42b/CD61). N=5 per stent. This preclinical ex vivo porcine shunt model used aspirin-only antiplatelet therapy.
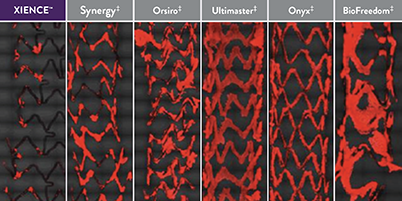
When Using Aspirin Monotherapy3
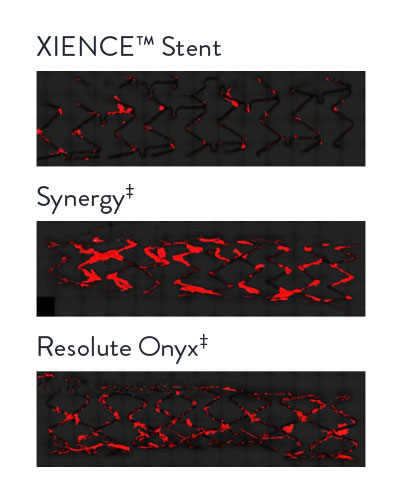
XIENCE™ Stent: Least Blood Platelet Adhesion (p < 0.05) When Using P2Y12 Inhibitor Monotherapy3
Representative confocal photomicrographs stained for platelets (CD42b/CD61). N=8 per stent. This preclinical ex vivo porcine shunt model used clopidogrel-only antiplatelet therapy.
XIENCE™ Stent: Least Blood Platelet Adhesion When Using Heparin Only14
Expert's Point of View: Reduced Inflammatory Response
In the images “on the right you can see the [pro-thrombotic] platelet adherence. XIENCE™ Stent [the image at the bottom] has hardly any attachments to it.” — Renu Virmani, MD, referring to the photomicrographs, where green indicates platelet adhesion.
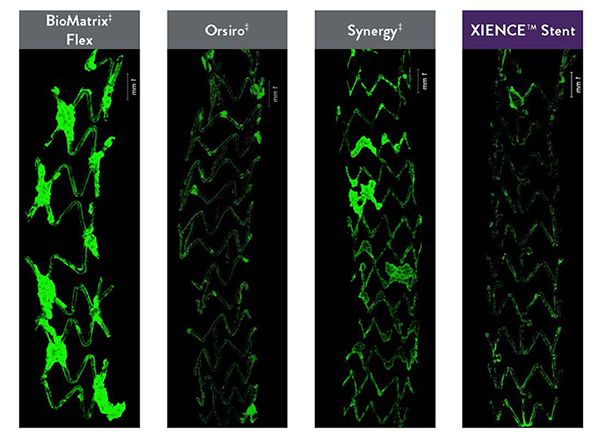
Visual Evidence of Fluoropolymer Safety
In several analyses, XIENCE™ Stent exhibits the most thromboresistance when compared to several different BP-DES.3,14
Least Thrombus Area with XIENCE™ Stent vs BP-DES14
Ex vivo porcine photomicrographs reveal the least thrombus area on XIENCE™ Stent (green areas are platelets).
Real-Time Platelet-Device Interaction
CVPath Institute also conducted tests to show real-time platelet-device interaction between different types of stents.
Compared with Synergy‡
Compared with Other DES
This preclinical model used in vitro human blood with heparin only. Representative confocal photomicrographs stained for platelets. Real-time platelet-device interaction was visualized under confocal microscopy and recorded in a time-lapse video. Image processing quantified platelet deposition on devices.
References
- Zanchin C, et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12(17):1665-1675. Serruys P, et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:136-146. Shiomi H, et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:637-647. Kufner S, et al. Circulation. 2019:139(3):325-333. Palmerini T, et al. Lancet. 2013;379:1393-1402. Bangalore S, et al. Circulation. 2012;125:2873-2891. Bangalore S, et al. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;6(6):378-390. Pilgrim T, et al. Lancet. 2014;384:2111-2122. Pilgrim T, et al. Lancet. 2018;392:737-746. Data on file at Abbott.
- Garfinkle AM, et al. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1984;30:432-439. Ao PY, et al. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2000;20:241-249. Jinnouchi H, et al. EuroIntervention. 2020;EIJ-D-19-00938.
- Jinnouchi H, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:(Suppl B):TCT-291. Sato Y, et al. PCR eCourse 2020.
- Szott LM, et al. Biointerphases. 2016;11:029806. Wertz CF, et al. Langmuir. 2001;17:3006-3016. Joner M, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008 Jul, 52 (5) 333-342.
- Panchalingam V, et al. ASAIO J. 1993;39:M305-M309.
- Paton DM, et al. U.S. Patent 5,356,668. Garfinkle AM, et al. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1984;30:43-439.
- Szott LM, et al. Biointerphases. 2016;11:029806.
- Mehran R, et al. TCT Connect 2020, XIENCE 28/90.
- Data on file at Abbott.
- Panchalingam V, et al. ASAIO J. 1993;39:M305-M309. Jinnouchi H, et al. EuroIntervention. 2020;EIJ-D-19-00938.
- Wu Y, et al. J Biomed Mater Res. 2005;74(4):722-738. Tsai WB, et al. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999:44:130-139.
- Garfinkle AM, et al. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1984;30:432-439.
- Kamberi M, et al. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(5):1721-1729. Zanchin, C. et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12(17):1665-1675. Serruys P, et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:136-146. Shiomi H, et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12(7):637-647. Kufner S, et al. Circulation. 2019:139(3):325-333.
- Otsuka F, et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8:1248-1260.
MAT-2101781 v2.0
