Supera™ Peripheral Stent
The Supera™ Peripheral Stent is indicated for the superficial femoral artery (SFA) and the proximal popliteal artery. Engineered by a unique interwoven wire technology, this nitinol stent offers physicians unmatched clinical outcomes5-16 across varied lesion complexities and lengths.1-4
To learn more about Supera™ Stent, simply request a free demonstration and your local Abbott representative will be in touch shortly.
Results Matter
The Supera™ Stent is known for the excellence of its clinical outcomes during percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) procedures, since this peripheral stent has been studied in more than 2,000 patients and 17 studies worldwide.3,5-16
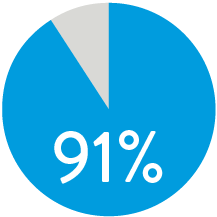
PATENCY (K-M) AT 1 YEAR5
When nominally deployed*
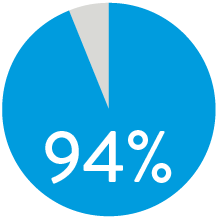
FREEDOM FROM TLR AT 3 YEARS5
When nominally deployed*
*Nominal deployment is defined as the stent length upon deployment being within +/- 10% of the labeled stent length. This data is from a non-powered post-hoc analysis.
Demonstrates excellent clinical outcomes
Supera™ Stent demonstrated excellent 1 yr patency and 3 yr freedom from TLR in the SUPERB trial.5
1
Unmatched clinical outcomes
Demonstrated unmatched clinical outcomes in simple lesions across US pivotal stent trials5-20
2
Consistent across lesion length
Exhibits consistent 1-year primary patency results regardless of lesion length17-25
3
Strong outcomes in calcification
Reveals strong clinical outcomes in severely calcified lesions at year 3 years5
* Study reported a majority with Trans-Atlantic Inter-Society Consensus Document (TASC) A & B lesions and/or Rutherford class 2 or 3 lesions
Design Matters
Unlike any other stent design platform, the Supera™ Stent is uniquely designed to keep vessels open with its distinct platform, created by interwoven individual, flexible nitinol wires
High Compression Resistance26
4x greater strength for compression resistance—so it can maintain a round, open lumen, which can be especially beneficial in calcified lesions
Low Chronic Outward Force26
With 1:1 stent to vessel sizing, low chronic outward force results in minimal vessel injury28
High Flexibility27 and Fracture Resistance5
Unparalleled flexibility,27 which mimics the natural structure and movement of the anatomy29-31
Zero stent fractures reported at 1 year in over 2,000 patients across 17 studies3,5-20
References
- Treitl, K.M., et al. European Radiology.2017; 10.1007.
- Garcia L. et al., Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 2017 Jun 1;89(7):1259-1267
- Brescia AA. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2015 Jun;61(6):1472-8
- Palena L.M. et al. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Intervention.2016.
- Garcia L. et al., Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 2017 Jun 1;89(7):1259-1267.
- Gray W. et al., Lancet 2018;392:1541-51.
- Dake M. et al., Circulation. 2016;133:1472-1483.
- Laird J. et al., Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2010;3:267-276.
- Laird J et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2012;19:1–9.
- S.M.A.R.T. Control IFU.
- Jaff, M., SMART Nitinol Self-Expanding Stent in the Treatment of Obstructive Superficial Femoral Artery Disease: Three-year Clinical Outcomes from the STROLL Trial. ISET 2014.
- Matsumura J et al., J Vasc Surg 2013;58:73-83.
- Rocha-Singh, K., 3-Year Results of the DURABILITY II Study. VIVA 2013.
- US Innova IFU.
- US Pulsar IFU.
- Ohki T. et al. J Vasc Surg. 2016 Feb;63(2):370-6.
- Treitl, K.M., et al. European Radiology. 2017; 10.1007
- Garcia L. et al. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8:e000937
- Scheinert D. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2011 Dec;18(6):745-52.
- San Norberto EM. et al., Ann Vasc Surg. 2017 May;41:186-195.
- Werner M. et al., EuroIntervention. 2014 Nov;10(7):861-8.
- George JC. et al., J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014 Jun;25(6):954-61.
- Montero-Baker M. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2016 Oct;64(4):1002-8.
- Brescia A. et al. J Vasc Surg. 2015 Mar 6. pii: S0741-5214(15)00132-9
- Palena L.M. et al. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 2016
- Competitors tested include Astron Pulsar-18, Complete SE, EverFlex, Innova, LifeStent, Misago, S.M.A.R.T., and Zilver PTX. Data on file at Abbott.
- Flexibility is defined as kink resistance. Competitors tested include Astron Pulsar-18, Complete SE, EverFlex, Innova, LifeStent, Misago, S.M.A.R.T., and Zilver PTX. Data on file at Abbott
- Zhao HQ et al. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2009;32(4):720-6
- Arena F. et al., J Vasc Med Surg. 2013:1;116.
- Chan Y. et al., J Vasc Surg 2014;59:384-91.
- Data on file at Abbott
MAT-2109821 v2.0
Supera™ Peripheral Stent System
Indications
The Supera™ Peripheral Stent System is indicated to improve luminal diameter in the treatment of patients with symptomatic de novo or restenotic native lesions or occlusions of the superficial femoral artery (SFA) and / or proximal popliteal artery with reference vessel diameters of 4.0 to 7.5 mm, and lesion lengths up to 140 mm.
Contraindications
The Supera™ Peripheral Stent System is contraindicated in:
- Patients who are judged to have a lesion that prevents complete inflation of an angioplasty balloon or proper placement of the stent or stent delivery system.
- Patients who cannot receive antiplatelet or anticoagulation therapy. Based on in vivo thrombogenicity testing, the device should not be used in patients who cannot be anticoagulated as there may be some thrombus formation in the absence of anticoagulation.
Warnings
- This device is intended for single-use only. Do not reuse. Do not resterilize. Do not use if the package is opened or damaged.
- Use this device prior to the “Use By” date as specified on the device package label. Store in a dry, dark, cool place.
- DO NOT use if it is suspected that the sterility of the device has been compromised.
- Persons with known hypersensitivities to Nitinol and / or its components (e.g. nickel-titanium) may suffer an allergic reaction to this implant.
- Administer appropriate antiplatelet therapy pre- and post-procedure.
- Careful attention should be paid when sizing and deploying the stent to prevent stent elongation. In the SUPERB clinical study, stent elongation was associated with a decrease in patency at 12 months.
Precautions
The Supera™ Peripheral Stent System should only be used by physicians and medical personnel trained in vascular interventional techniques and trained on the use of this device.
- The long-term safety and effectiveness of the Supera™ Peripheral Stent System has not been established beyond three years.
- The safety and effectiveness of the Supera™ Peripheral Stent System has not been established in patients who:
- are less than 18 years old
- are pregnant or lactating
- have in-stent restenosis of the target lesion
- have known hypersensitivity to any component of the stent system (e.g., nickel)
- cannot tolerate contrast media and cannot be pre-treated
- have uncontrolled hypercoagulability and / or another coagulopathy
- This device is not designed for use with contrast media injection systems or power injection systems.
- The flexible design of the Supera™ stent may result in variation in the deployed stent length.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Safety Information
Nonclinical testing has demonstrated that the Supera™ stent, in single and in overlapped configurations up to 250 mm in length, is MR Conditional. A patient with this device can be safely scanned in an MR system meeting the following conditions:
- Static magnetic field of 1.5 or 3.0 Tesla
- Maximum spatial gradient magnetic field of 2,500 Gauss/cm (25 T/m)
- Maximum MR whole-body-averaged specific absorption rate (SAR) of
- 2 W/kg for landmarks (i.e. center of RF coil) above the umbilicus
- 1 W/kg for landmarks below the umbilicus and above the mid-thigh
- 0.5 W/kg for landmarks below the mid-thigh
Under the scan conditions defined above, the Supera™ stent is expected to produce a maximum temperature rise of 7.6 °C after 15 minutes of continuous scanning.
In nonclinical testing, the image artifact caused by the device extends approximately 2 cm from the Supera™ stent when imaged with a gradient echo or spin echo sequence and a 3T MRI system.
Potential Adverse Events
Potential adverse events include, but are not limited to:
- Abrupt closure
- Allergic reaction (contrast medium; drug; stent material)
- Amputation or limb loss
- Aneurysm or pseudoaneurysm in vessel or at vascular access site
- Angina or coronary ischemia
- Arrhythmia (including premature beats, bradycardia, atrial or ventricular tachycardia, atrial or ventricular fibrillation)
- Arteriovenous fistula
- Bleeding complications requiring transfusion or surgical intervention
- Death
- Detachment of a system component or implantation in an unintended site
- Embolization, arterial or other (e.g. air, tissue, plaque, thrombotic material, or stent)
- Emergent surgery
- Fever
- Hematoma or hemorrhagic event, with or without surgical repair
- Hyperperfusion syndrome
- Hypertension / Hypotension
- Infection
- Myocardial infarction
- Pain (leg, foot, and/or insertion site)
- Partial stent deployment
- Peripheral nerve injury
- Pulmonary embolism
- Renal failure or insufficiency
- Restenosis of vessel in stented segment
- Shock
- Stent malapposition or migration, which may require emergency surgery to remove stent
- Stent strut fracture
- Thrombosis or occlusion
- Stroke
- Transient ischemic attack
- Venous thromboembolism
- Vessel dissection, perforation or rupture
- Vessel spasm or recoil
- Worsening claudication or rest pain
MAT-2103597 v3.0
