Supera™ Peripheral Stent
The Supera™ Peripheral Stent is a unique class of SFA Technology. Engineered with an innovative interwoven wire technology, this nitinol stent offers physicians unmatched clinical outcomes1-12 across varied lesion complexities and lengths.1, 13-15
Results Matter
The Supera™ Stent is known for the excellence of its clinical outcomes after percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) procedures with stent placement, since this peripheral stent has been studied in more than 2,000 patients and 17 studies worldwide.1,15-30
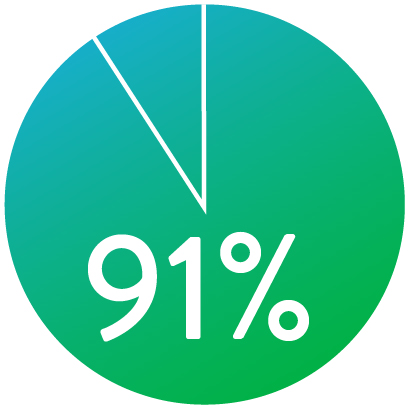
PATENCY (K-M) AT 1 YEAR
When nominally deployed*
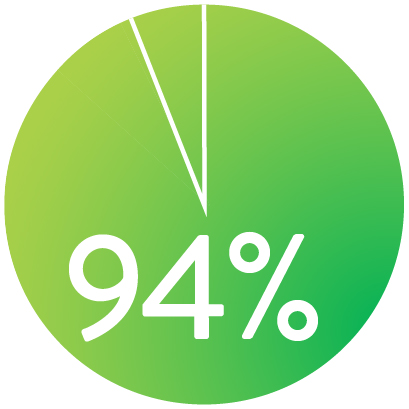
FREEDOM FROM TLR AT 3 YEARS
When nominally deployed*
*Nominal deployment is defined as the stent length upon deployment being within +/- 10% of the labeled stent length. This data is from a non-powered post-hoc analysis.
Demonstrates excellent clinical outcomes
Supera™ Stent demonstrated excellent 1 yr patency and 3 yr freedom from TLR in the SUPERB trial.1
1
Unmatched clinical outcomes
Demonstrated unmatched clinical outcomes in simple lesions1-12
2
Consistent patency regardless of lesion length*
Exhibits consistent 1-year primary patency results regardless of lesion length13-20,31
3
Strong outcomes in calcification
Reveals strong clinical outcomes in severely calcified lesions at year 3 years1
Study reported 93.8% with Trans-Atlantic Inter-Society Consensus Document (TASC) A & B lesions and/or Rutherford class 2 or 3 lesions
*Patency rates have been evaluated in studies in lesion lengths ranging from 5.3 cm to 28.0 cm.
Platform Matters
Unlike any other stent design platform, the Supera™ Stent is uniquely designed to keep vessels open with its distinct platform, created by interwoven individual, flexible nitinol wires.
High Compression Resistance32
4x greater strength for compression resistance—so it can maintain a round, open lumen, which can be especially beneficial in calcified lesions
Low Chronic Outward Force32
With 1:1 stent to vessel sizing, low chronic outward force results in minimal vessel injury34
High Flexibility33 and Fracture Resistance1
Unparalleled flexibility,33 which mimics the natural structure and movement of the anatomy35-37
Zero stent fractures reported at 1 year in over 2,000 patients across 17 studies1,15-30
REFERENCES
- Garcia L. et al., Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 2017 Jun 1;89(7):1259-1267.
- Dake M. et al., Circulation. 2016;133:1472-1483.
- Laird J. et al., Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2010;3:267-276.
- Laird J et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2012;19:1–9.
- S.M.A.R.T. Control IFU.
- Jaff, M., SMART Nitinol Self-Expanding Stent in the Treatment of Obstructive Superficial Femoral Artery Disease: Three-year Clinical Outcomes from the STROLL Trial. ISET 2014.
- Matsumura J et al., J Vasc Surg 2013;58:73-83.
- Rocha-Singh, K., 3-Year Results of the DURABILITY II Study. VIVA 2013.
- US Innova IFU.
- US Pulsar IFU.
- Ohki T. et al. J Vasc Surg. 2016 Feb;63(2):370-6.
- Gray W. et al., Lancet 2018;392:1541-51.
- Treitl, K.M., et al. European Radiology. 2017; 10.1007.
- Palena L.M. et al. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Intervention. 2016.
- Brescia AA. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2015 Jun;61(6):1472-8
- George JC. et al., J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014 Jun;25(6):954-61.
- Montero-Baker M. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2016 Oct;64(4):1002-8.
- Scheinert D. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2011 Dec;18(6):745-52.
- Werner M. et al., EuroIntervention. 2014 Nov;10(7):861-8.
- San Norberto EM. et al., Ann Vasc Surg. 2017 May;41:186-195.
- Chan YC. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2015 Nov;62(5):1201-9.
- Dumantepe M. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2017 Jul;51(5):240-246.
- Goltz JP. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2012 Jun;19(3):450-6.
- León LR Jr. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2013 Apr;57(4):1014-22.
- Myint M. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2016 Jun;23(3):433-41.
- Palena LM. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2018 Oct;25(5):588-591.
- Scheinert D. et al., JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013 Jan;6(1):65-71.
- Steiner S. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2016 Apr;23(2):347-55.
- Teymen B. et al., Vascular. 2018 Feb;26(1):54-61.
- Bhatt H. et al., Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2018 Jul;19(5 Pt A):512-515.
- Garcia L. et al. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8:e000937
- Competitors tested include Astron Pulsar-18, Complete SE, EverFlex, Innova, LifeStent, Misago, S.M.A.R.T., and Zilver PTX. Data on file at Abbott.
- Flexibility is defined as kink resistance. Competitors tested include Astron Pulsar-18, Complete SE, EverFlex, Innova, LifeStent, Misago, S.M.A.R.T., and Zilver PTX. Data on file at Abbott.
- Zhao HQ et al. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2009;32(4):720-6
- Arena F. et al., J Vasc Med Surg. 2013:1;116.
- Chen Y. et al., J Vasc Surg 2014;59:384-91.
- Data on file at Abbott.
MAT-2106530 v2.0

