OCT with MLD MAX Workflow Improves PCI Decision-Making, Safety and Procedural Efficiency1
OCT with MLD MAX workflow changed physician PCI decision-making in 86% of lesions compared to angiography.1

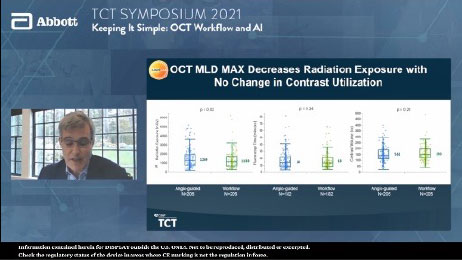
OCT with MLD MAX workflow reduced radiation exposure by 10.7% with no difference in contrast use compared to angiography.2

Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is mostly guided by angiography which has well-established limitations:
- Inaccurate visual estimation of luminal dimensions1
- Little to no information on plaque morphology, vascular remodeling, or atherosclerosis burden1
- Inability to detect underexpansion, malapposition and edge dissection1
Multi-phase LightLab data gives further insights into the limitations of angiography in the cath lab and highlights the benefits of using intravascular imaging with OCT.
What is LightLab?
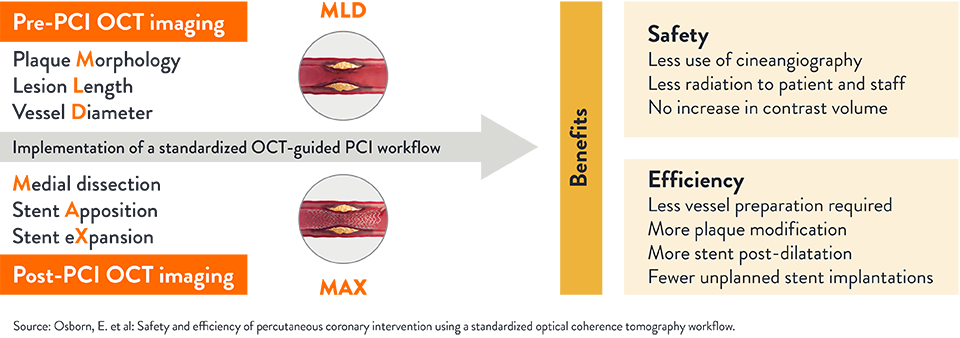
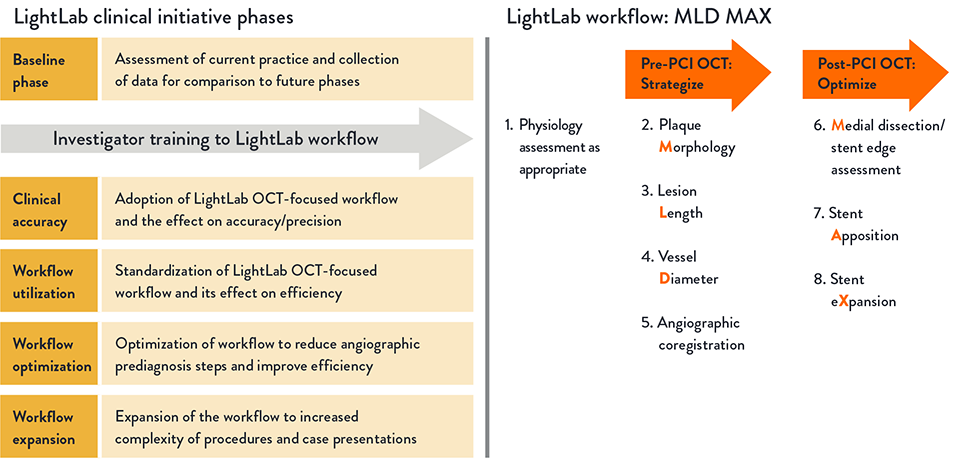
The LightLab Clinical Initiative (“LightLab”) is a multicenter, prospective, observational clinical initiative designed to evaluate the impact of using a standardized OCT workflow, MLD MAX, on physician decision-making and procedural efficiency.
The workflow facilitates utilization of OCT information to guide treatment decisions during PCI: assessment of lesion Morphology, Length, and Diameter (MLD) from pre-PCI OCT pullback and optimization of stent placement for Medial dissection, stent Apposition, and stent Xpansion (MAX) from the post-PCI OCT pullback.
How Does OCT with MLD MAX Impact PCI Decision-Making?
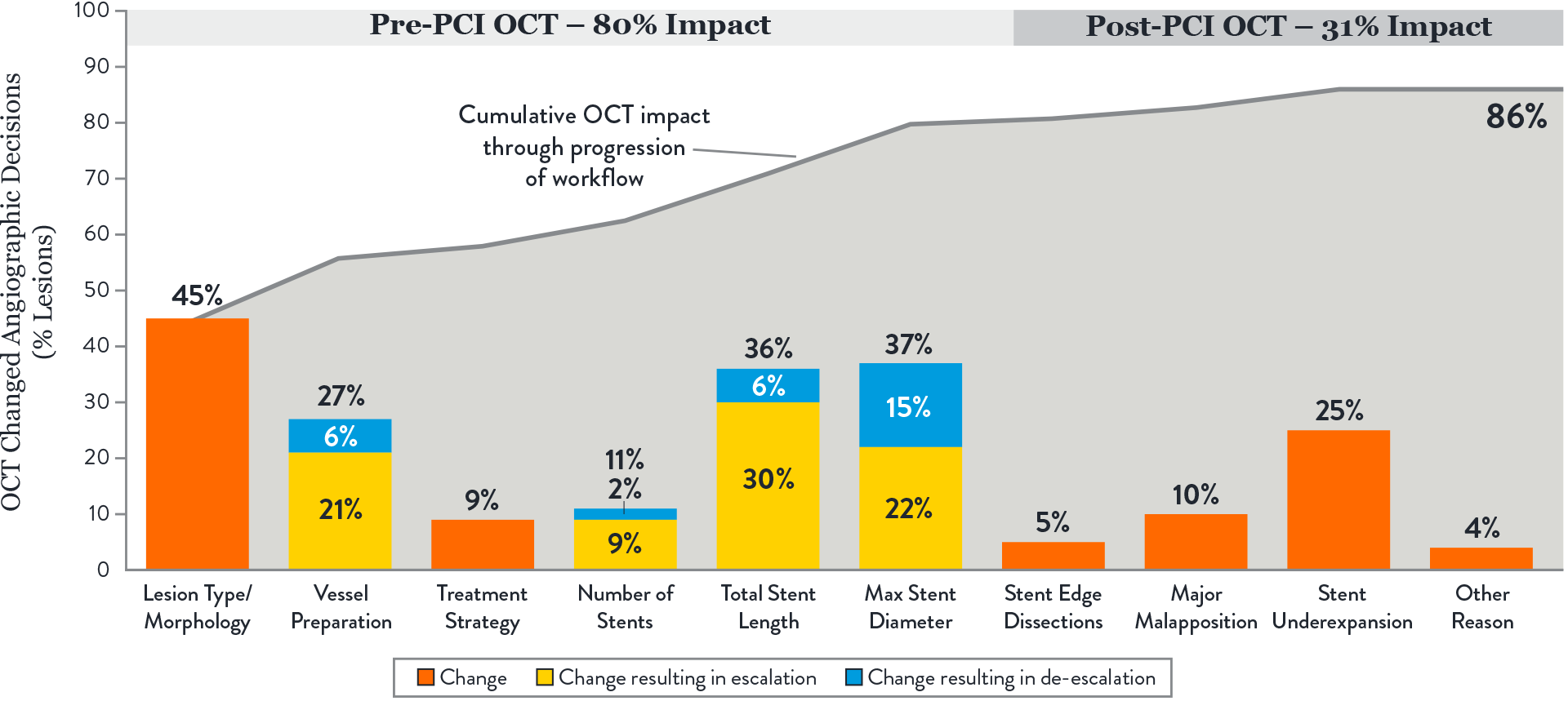
OCT with MLD MAX workflow changed physician PCI decision-making in 86% of lesions compared to angiography.1 The impact of OCT was consistent regardless of operator’s prior OCT experience.1
Key takeaways:
- The largest impact of OCT-guided assessment over angiography was observed prior to stenting, in pre-PCI OCT or MLD steps.1
These steps involve morphology assessment (M), stent sizing (L&D) and vessel preparation, key decisions which may influence final stent expansion. Achieving optimal expansion is proven to reduce rates of major adverse cardiac events during PCI.3
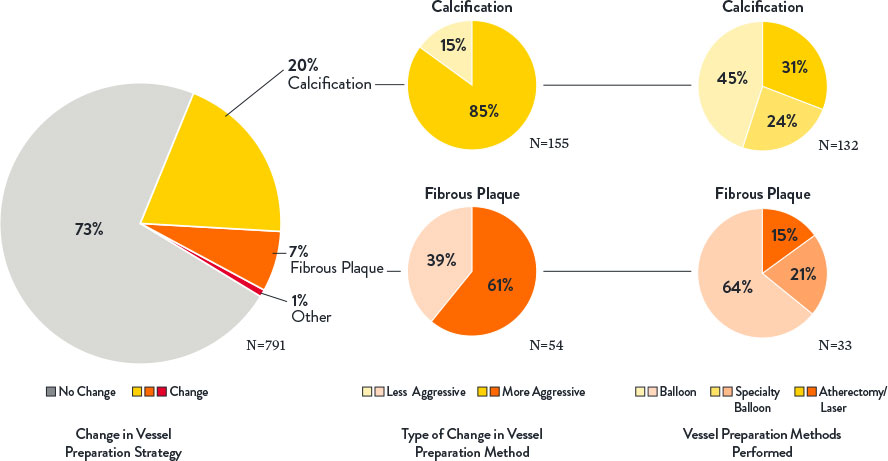
- OCT changed angio-based assessment of lesion morphology in 45% of lesions and subsequently impacted vessel prep strategy.1
OCT provides additional information on lesion morphology (plaque type composition) which informs how to prepare and treat the vessel appropriately, especially when calcification is present. Severity of calcification was underestimated in 85% of lesions when using angiography alone. Extensive calcification may adversely impact PCI procedure and final stent expansion.3
- Optimal stent expansion was achieved with MLD MAX workflow.1
The use of MLD MAX workflow helped achieve 80% stent expansion on average compared to 76% average stent expansion in lesions before stent optimization. Data from trials and registries have demonstrated that achieving a minimal stent area >4.5 mm2 and/or a stent expansion of >80% using OCT is associated with lower major adverse clinical events.4
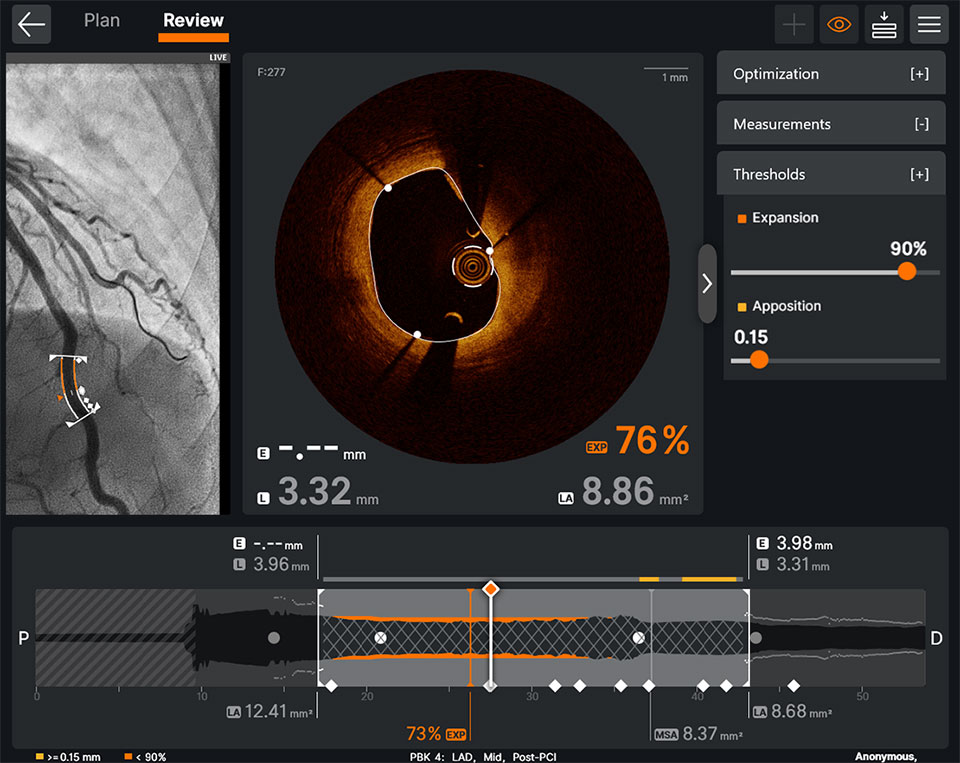
OCT makes it easy to detect underexpansion. Ultreon™ Software displays instantaneous calculations of expansion and apposition values, reference lumen diameter and lumen diameter values in color-coded markers: stent underexpansion indicator—orange, stent malapposition indicator—yellow.6
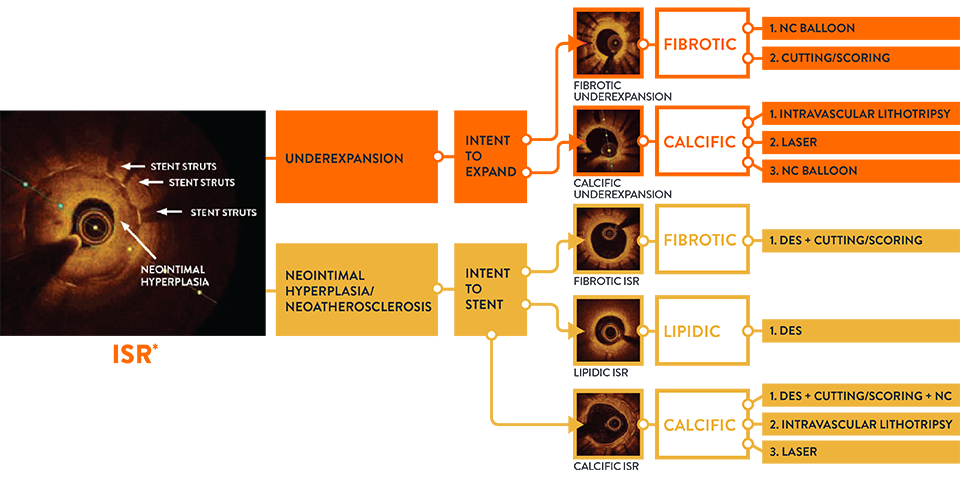
- Pre-PCI OCT changed angio-based diagnosis and treatment decisions in ISR lesions.7
When physicians used OCT pre-PCI in ISR lesions, they changed their angiographic diagnosis and treatment strategy in 91% of lesions. OCT can identify ISR and the mechanism of stent failure which impacts ISR treatment strategy. In LightLab, OCT changed angio assessment of ISR mechanism in 48% of lesions.
Identifying the mechanism of stent failure is paramount to planning treatment because treatment strategy is different for ISR due to stent underexpansion and ISR due to neointimal hyperplasia.3 Analysis of ISR by intravascular imaging is essential to understand the mechanism of failure and OCT is a preferred technique.3
How Does OCT With MLD MAX Impact PCI Safety and Efficiency?
OCT with MLD MAX reduced radiation exposure by 10.7% with no difference in contrast use.2
Implementing OCT with MLD MAX workflow pre- and post-PCI improves PCI safety and efficiency compared to PCI guided by angiography alone.2
Key takeaways:
- OCT with MLD MAX reduces radiation exposure by 10.7% and improves procedural safety.2
The detailed information provided by OCT diminishes reliance on angiography, resulting in fewer cineangiography runs (and no difference in contrast use) and less overall case radiation to patient and cath lab staff.2
- OCT with MLD MAX improves procedural efficiency.2
The detailed information provided by OCT decreased the need for universal vessel preparation and improved device selection based on proper plaque modification and precise stent sizing selection.2
When operators use OCT with the full MLD MAX workflow (pre-PCI OCT and post-PCI OCT) vs performing post-PCI OCT only, procedural benefits include reduced rate of underexpansion and malapposition, reduced use of contrast and decreased need for further optimization.5
Compared to PCI performed by angiography guidance alone, implementing an OCT-guided MLD MAX workflow decreased radiation exposure with no difference in contrast utilization and enhanced procedural efficiency by guiding proper device selection, leading to less product utilization and fewer unplanned treatments.
OCT imaging with MLD MAX workflow supports complete vessel evaluation, proper lesion preparation and optimization which are critical to achieve optimal stent expansion. Inadequate stent expansion is the most important predictor of subsequent stent failure due to stent thrombosis (ST) or restenosis.2
About LightLab Study
LightLab structure and phases
LightLab is a multiphase prospective observational data-gathering study conducted between January 2019 and June 2021, with 17 participating hospitals and physicians in the US. Data were gathered in real-time, where OCT guidance was employed during PCI using a standardized OCT-guided workflow MLD MAX.
The LightLab Clinical Initiative was designed in multiple phases to facilitate regular adoption of the MLD MAX workflow during PCI to improve operator and procedural efficiency, and to expand the workflow into increasingly complex procedures.
References
- Bergmark, B. et al: Decision-Making During Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Guided by Optical Coherence Tomography: Insights From the LightLab Initiative. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2022;15:e011851. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.122.011851.
- Osborn, E. et al: Safety and efficiency of percutaneous coronary intervention using a standardized optical coherence tomography workflow. EuroIntervention 2023;18:1178-1187. DOI: 10.4244/EIJ-D-22-00512.
- Räber, L. et al. Clinical use of intracoronary imaging. Part 1: guidance and optimization of coronary interventions. An expert consensus document of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(35):3281-3300.
- Razzouk, L. et al. Workflow for Percutaneous Coronary Intervention With Optical Coherence Tomography-Guidance: MAXing the MLD? Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions. Retrieved from: http://ahajournals.org on November 16, 2022.
- Khuddus, M. et al. Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory Efficiency and Quality Improvement during Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Utilizing a Standardized Optimal Coherence Tomography (OCT) Workflow in a Real-World Setting: Results from the LightLab Initiative. CRTOnline 2021.
- Ultreon™ 2.0 Software Instructions For Use (IFU). Refer to Instructions IFU for additional information.
- Croce, K., et al: Effect of a Prescriptive Optical Coherence Tomography Guided Strategy on Treatment of In-Stent Restenosis – Insights from the LightLab Initiative. TCTConnect2020 Presentation.
MAT-2113909 v3.0
OPTIS™ and OPTIS™ Next Imaging Systems and Software
INDICATIONS
Applies to OPTIS™ Imaging Systems and Software
The OPTIS™ Software and AptiVue™ E Series Software are intended to be used only with compatible OPTIS™ Imaging Systems.
The OPTIS™ Imaging Systems with a compatible Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheter are intended for the imaging of coronary arteries and is indicated in patients who are candidates for transluminal interventional procedures. The compatible Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters are intended for use in vessels 2.0 to 3.5 mm in diameter. The compatible Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters are not intended for use in the left main coronary artery or in a target vessel which has undergone a previous bypass procedure.
The OPTIS™ Imaging Systems are intended for use in the catheterization and related cardiovascular specialty laboratories and will further compute and display various physiological parameters based on the output from one or more electrodes, transducers, or measuring devices. The physician may use the acquired physiological parameters, along with knowledge of patient history, medical expertise and clinical judgment to determine if therapeutic intervention is indicated.
Applies to OPTIS™ Next Imaging Systems and Software
The Ultreon™ 1.0 Software and Ultreon™ 2.0 Software are intended to be used only with compatible OPTIS™ Next Imaging Systems.
The OPTIS™ Next Imaging System with a compatible Dragonfly™ OPTIS™ Imaging Catheter or Dragonfly OpStar™ Imaging Catheter is intended for the imaging of coronary arteries and is indicated in patients who are candidates for transluminal interventional procedures. The Dragonfly™ OPTIS™ Imaging Catheter or Dragonfly OpStar™ Imaging Catheter is intended for use in vessels 2.0 to 3.5 mm in diameter. The Dragonfly™ OPTIS™ Imaging Catheter or Dragonfly OpStar™ Imaging Catheter is not intended for use in the left main coronary artery or in a target vessel which has undergone a previous bypass procedure.
The OPTIS™ Next Imaging Systems are intended for use in the catheterization and related cardiovascular specialty laboratories and will further compute and display various physiological parameters based on the output from one or more electrodes, transducers, or measuring devices. The physician may use the acquired physiological parameters, along with knowledge of patient history, medical expertise, and clinical judgment to determine if therapeutic intervention is indicated.
Applies to both OPTIS™ and OPTIS™ Next Imaging Systems and Software
The Dragonfly™ OPTIS™ or Dragonfly™ OpStar™ Imaging Catheters are intended for use in vessels 2.0 to 3.5 mm in diameter. The Dragonfly™ OPTIS™ or Dragonfly™ OpStar™ Imaging Catheters are not intended for use in the left main coronary artery or in a target vessel which has undergone a previous bypass procedure.
The OPTIS™ and OPTIS™ Next Imaging Systems are intended for use in the catheterization and related cardiovascular specialty laboratories and will further compute and display various physiological parameters based on the output from one or more electrodes, transducers, or measuring devices. The physician may use the acquired physiological parameters, along with knowledge of patient history, medical expertise, and clinical judgment to determine if therapeutic intervention is indicated.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
The OPTIS™ and OPTIS™ Next Integrated Systems and Mobile Systems with the usage of the OPTIS™ Software, AptiVue™ E Series Software, Ultreon™ 1.0 Software, and Ultreon™ 2.0 Software are contraindicated where introduction of any catheter would constitute a threat to patient safety. Contraindications include:
- Bacteremia or sepsis
- Major coagulation system abnormalities
- Patients diagnosed with coronary artery spasm
- Patients disqualified for coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery
- Patients disqualified for percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA)
- Severe hemodynamic instability or shock
- Total occlusion
- Large thrombus
- Acute renal failure
- Inability to tolerate systemic anticoagulation is a contraindication to use of OCT for coronary imaging.
- The system has no patient alarm functions. Do not use for cardiac monitoring.
COMPLICATIONS
The following complications may occur as a consequence of intravascular imaging and catheterization procedure:
- Abnormal heart rhythm or arrhythmias
- Acute myocardial infarction
- Allergic reaction to the contrast media or drug administered for the procedure
- Arterial dissection, injury, or perforation
- Bleeding
- Catheter access site reactions: inflammation or granuloma
- Coronary artery spasm
- Death
- Embolism
- Hypotension
- Infection
- Myocardial ischemia
- Renal insufficiency or failure from contrast media use
- Repeat revascularization
- Thrombus formation, abrupt closure, or total occlusion
- Tissue necrosis
- Unstable angina
WARNINGS
- Prior to use, please review the Instructions for Use supplied with the OPTIS™ imaging system, Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheter, Wi-Box™ AO Transmitter and the PressureWire™ guidewire for more information.
- The Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheter is sterilized by ethylene oxide and is intended for one time use only. Non-pyrogenic. Do not use if the package is opened or damaged. Do not reuse or re-sterilize. Any attempt to reuse or re-sterilize may compromise the structural integrity of this device. Adverse effects of using a non-sterile or re-sterilized catheter may include, but are not limited to: local and / or systemic infection, mechanical damage, inaccurate results.
- Appropriate anticoagulant and vasodilator therapy must be used during the procedure as needed.
- Ensure that no air is introduced into the system during the Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters insertion.
- Observe all advancement and movement of the Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters under fluoroscopy. Always advance and withdraw the catheter slowly. Failure to observe device movement fluoroscopically may result in vessel injury or device damage. To ensure proper placement, do not move the guide wire after a Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheter is in place.
- If resistance is encountered during advancement or withdrawal of the Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheter, stop manipulation and evaluate under fluoroscopy. If the cause of resistance cannot be determined or mitigated, carefully remove the Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters and guidewire together as a unit from the patient.
- Leave the guide wire engaged with a Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheter at all times during use. Do not withdraw or advance the guide wire prior to withdrawing the Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters.
- The Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters should never be forced into lumens that are narrower than the Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters body or forced through a tight or heavily calcified lesion.
- The Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters should not be advanced through abnormally tortuous anatomy.
- When advancing or retracting a Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheter with a monorail tip through a stented vessel, the Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters may engage the stent between the junction of the Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters and guide wire, resulting in entrapment of catheter / guide wire, catheter tip separation, stent dislocation, and / or vascular injury.
- Refer to the contrast media Instructions for Use for general warnings and precautions relating to use of contrast media.
- Before creating an OCT recording, review “Performing an OCT Procedure” for additional warnings and cautions in the IFU.
PRECAUTIONS
- Safety and effectiveness have been established for the following patient population: adult patients undergoing non-emergent percutaneous coronary interventions in lesions with reference vessel diameters between 2.0 to 3.5 mm, which are not located in the left main coronary artery or in a target vessel which has undergone previous bypass procedures.
- Follow all instructions, warnings, and cautions provided in “Patient Safety” in the IFU.
- All operators must be knowledgeable in performing OCT and physiological procedures prior to using the OPTIS™ and OPTIS™ Next Integrated Systems and Mobile Systems with the usage of the OPTIS™ Software, AptiVue™ E Series Software, Ultreon™ 1.0 Software, and Ultreon™ 2.0 Software.
- When using saline, heparinized saline is recommended.
- Monitor the OCT image for indications of the Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters optical failure. If optical failure is suspected, remove the Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheter from the patient, press “Unload” on the drive motor and optical controller (DOC), detach the catheter, and replace it with a new one.
- If the pullback triggers before contrast is injected, repeat the pullback.
- For optimal imaging, only use 100% contrast media.
- Use the minimum flush rate and volume required to image the desired anatomy.
- To obtain accurate measurements, be sure the selection for the Flush Medium is the same as the medium in which you are imaging.
- The Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters must be purged prior to connection to the DOC to prevent damage to the imaging core.
- Do not insert or remove a Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheter while the DOC is scanning. Do not attempt to disconnect the catheter from the DOC while the “lock” LED is blinking as it could damage the catheter or the DOC. Refer to “Removing the Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheter” in the IFU.
- Never attempt to attach or detach a catheter to the DOC while the "lock" LED is lit.
- Take care in handling the Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters to prevent breaking the fiber-optics within the catheter. Kinking and bending of the catheter can cause damage. While connecting, ensure the proximal catheter segment is straight and aligned with the DOC. Never attempt to connect and operate the catheter while the catheter remains coiled within the hoop.
- Do not kink, sharply bend, pinch, or crush the Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters at any time.
- The Dragonfly™ Imaging Catheters have no user serviceable parts. Do not attempt to repair or alter any part of the catheter assembly as provided.
- If you want to make measurements on files that will be exported to standard formats, you must make the measurements BEFORE exporting the images. Using non-OCT software to measure standard format images will not produce accurate measurements.
- Do not use images that have been exported to JPEG or Compressed AVI formats for clinical decision making. These formats use compression methods that may degrade the image quality.
- Artifacts may result in misrepresentation of L-mode data, so L-mode is not recommended for quantification of clinical information.
- It is the user’s responsibility to confirm the lumen contours of all the frames within the reference segment, and to make adjustments if necessary. Red frames indicate low confidence in the detected contours.
- Deleted files cannot be restored. After files have been deleted, they can only be imported back to your system from your archived copies.
- Restoring factory default settings resets ALL user-entered configuration values except the date and time. This button should be used only under the direction of qualified service personnel.
MAT-2309288 v1.0