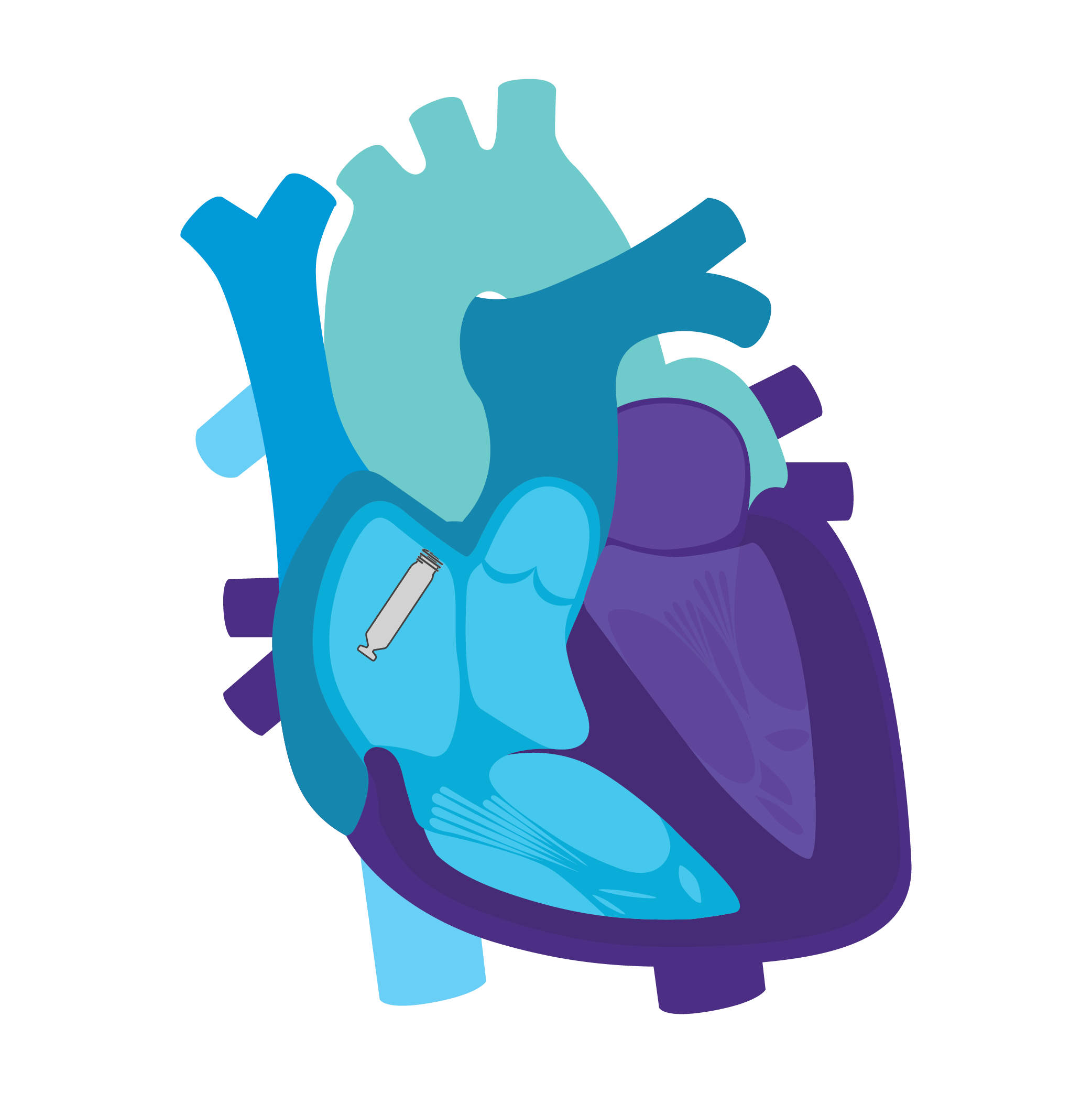
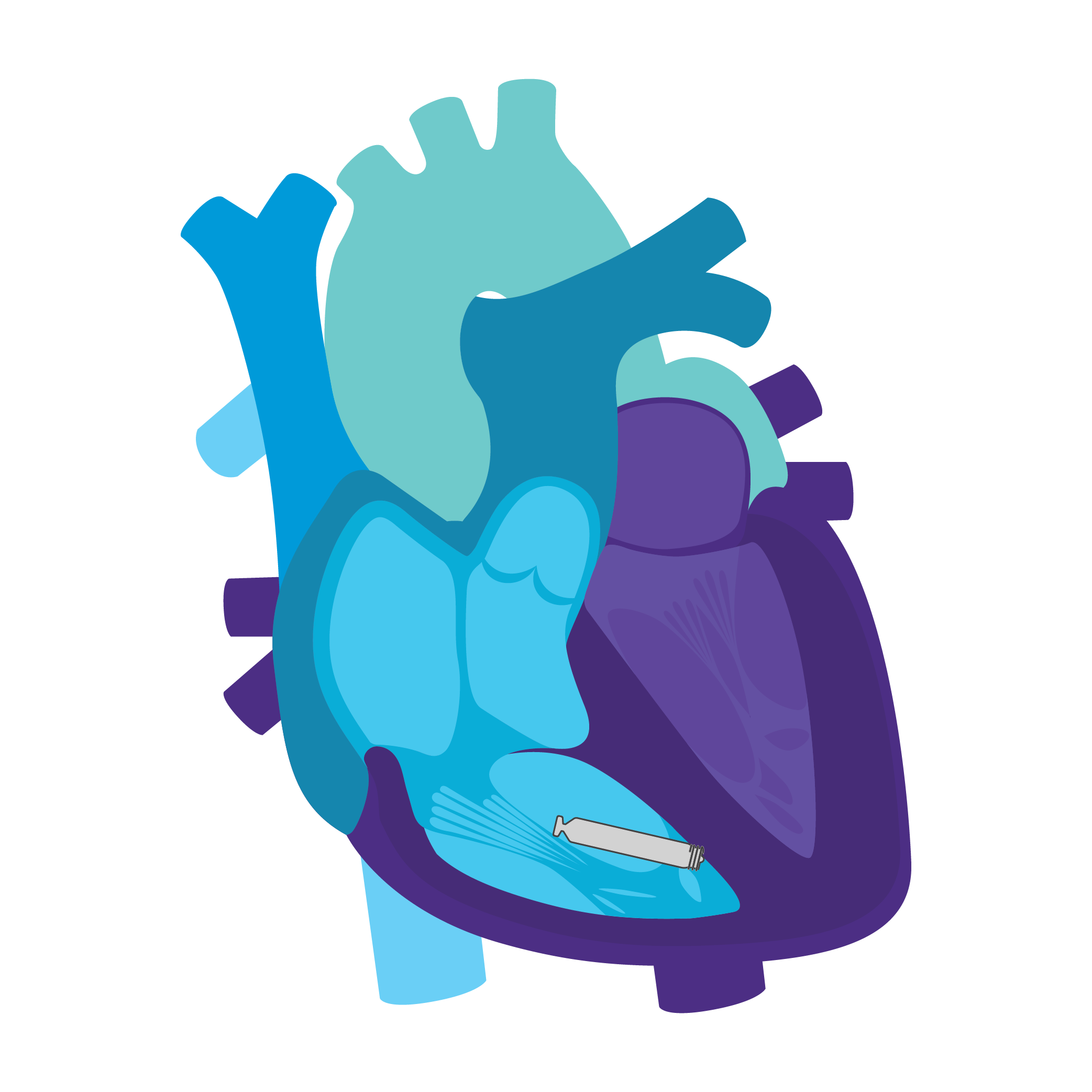
Setting the Pace with
AVEIR™ Leadless Pacemakers
Single and Dual Chamber Leadless Pacemaker Solutions, only from Abbott
MAT-2514762 v1.0 | Item approved for U.S. use only. ©2025 Abbott. All Rights Reserved.
Why AVEIR Leadless Pacemakers?
The leadless pacemaker system that offers tailored therapy and adaptability for your patient.
- Improved patient experience - no chest bumps or scars, no arm movement restrictions, faster recovery post-implant
- Reduction in device-related complications and reintervention risk at 6 months1
- Fewer pocket-related infections or lead-related complications
- Pre-fixation mapping capability – help reduce the number of repositioning attempts2
- Designed to be retrievable allowing replacement of the atrial or ventricular device as needed
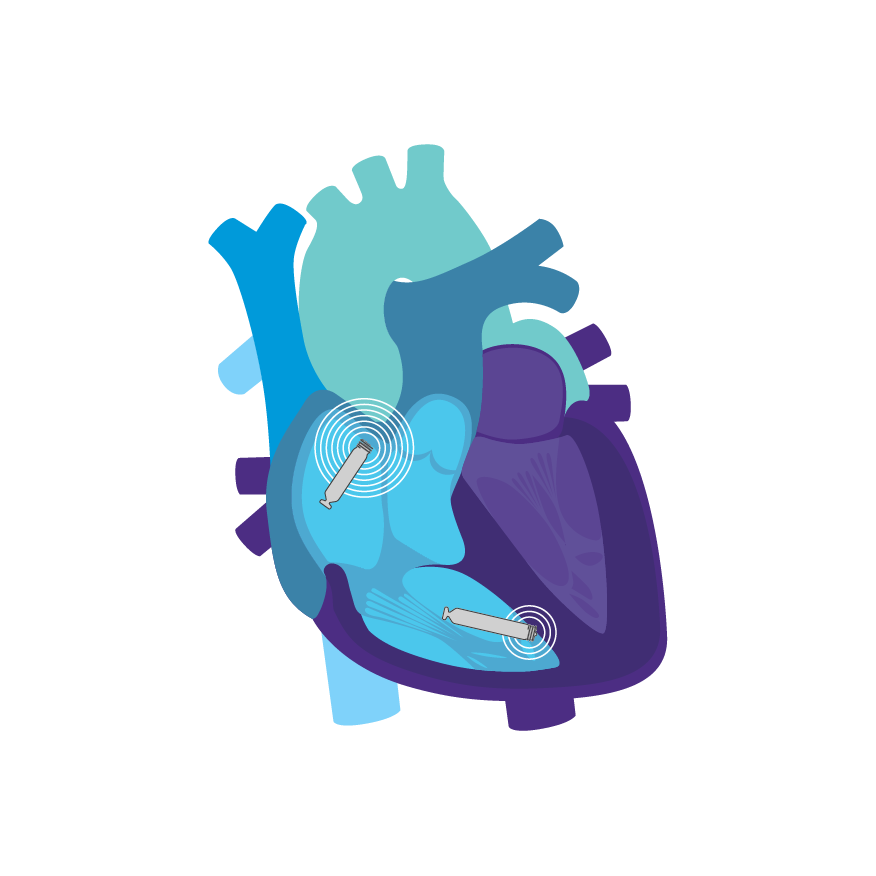
Tailored Leadless Pacing. Implant an atrial or ventricular device alone.
Or both combined.2
AVEIR AR2 Atrial LP. AVEIR VR Ventricular LP. Individually, they are capable of AAI(R) or VVI(R). But together they can provide the world's first leadless DDD(R) or AAI(R)+VVI† system. Tailor therapy by implanting one or both devices based on your patient’s indications and needs.
Learn more about the benefits of this system that is redefining the landscape of cardiac pacing below.
- Sinus node dysfunction and normal AV and intraventricular conduction systems
- Significant bradycardia and normal sinus rhythm with only rare episodes of AV block or sinus arrest
- Chronic atrial fibrillation
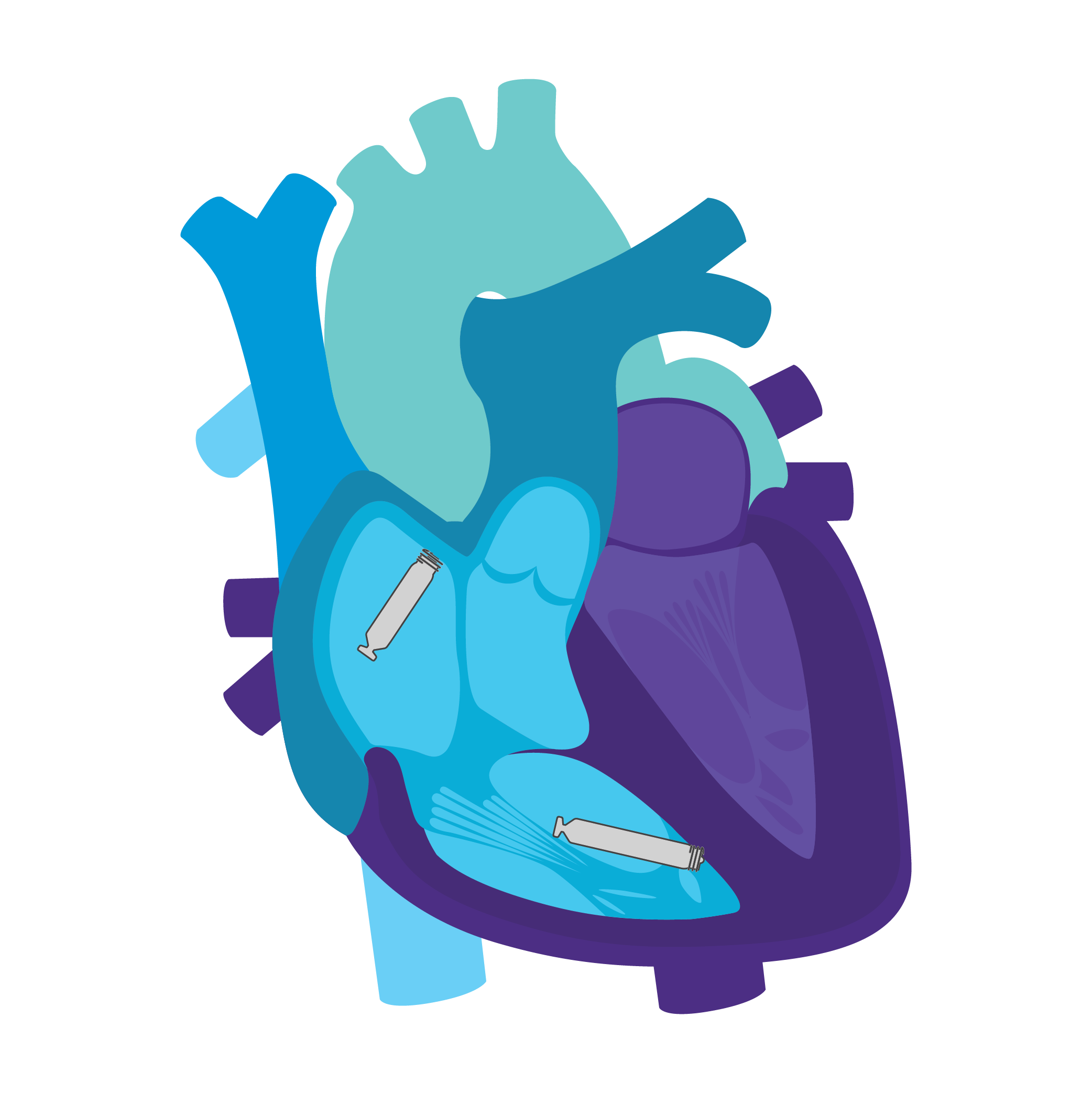
AVEIR™ DR DUAL CHAMBER LP SYSTEM
- Sick sinus syndrome
- Chronic, symptomatic 2nd-and 3rd-degree AV block
- Symptomatic bilateral bundle branch block when tachyarrhythmia and other causes have been ruled out
† Note: AAI(R)+VVI mode should not be used in patients without intact AV node conduction, or with chronic atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
Continuous AV, Beat-to-Beat Synchrony via Implant-to-Implant (i2i™) Technology2
To support dual chamber therapy, each implant communicates beat-to-beat with a paired, co-implanted device using i2i communication. This novel technology employs low energy, subthreshold pulses between implanted devices using the conductive nature of the body's blood pool and myocardial tissue. These high frequency pulses of data are delivered concurrently with each locally paced or sensed event, without impact on pacing or intrinsic sensing.
Upgradeable System2
With sensing and pacing in both the right atrium and right ventricle, you now have AAI(R), VVI(R), DDD(R) and AAI(R)+VVI leadless configurations to consider. You can match your patients' pacing needs today and then upgrade over time as those needs change.
Upgrade Pathways
Treatment option 1: Start with the atrial device.
Treat sinus node dysfunction today.
Add a ventricular device for heart block later.
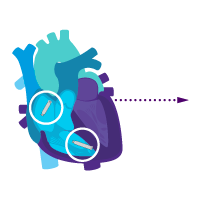
Enable i2i communication.

Activate dual chamber pacing therapy DDD(R) via i2i communication.
Treatment option 2: Start with the ventricular device.
Treat rare intermittent heart block today.
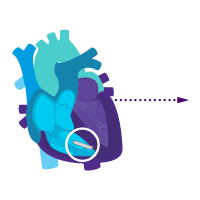
Add an atrial device for sick sinus syndrome later.

Enable i2i communication.

Activate dual chamber pacing therapy DDD(R) via i2i communication.

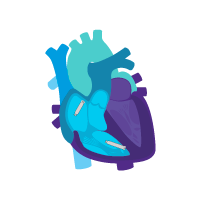
Treatment option 3: Start with a dual chamber DDD(R) system.
Start with a dual chamber system.
Turn off Beat-to-Beat communications to enable independent single chamber pacing for each device.

Treat SND patients today with AAI(R)+VVI pacing in the case of rare intermittent AV block.
- Up to 70% increase in atrial device longevity versus DDD(R)2,3,*
- Minimized/back-up ventricular pacing in the case of rare intermittent AV block
* 1.5V, 0.4 ms, 60 bpm, 300 ohms, 100% A pacing, 10% V pacing, i2i™ settings = 4 / 4
Download the Latest HRS 2025 Data Flyer
Discover How AVEIR™ LPs Are Transforming Cardiac Care
Long-Term Retrieval4
This allows for the replacement of the atrial or ventricular device at end of service (EOS) without leaving hardware behind.
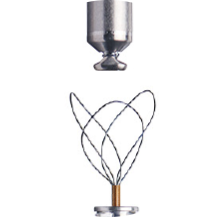
Specialty designed retrieval catheter supported by step-by-step protocol.
Through nine years regardless of implant duration, AVEIR VR Ventricular Leadless Pacemaker (LP) predecessor device has a long-term retrieval success rate of 88%.4

Active fixation helix uses a screw-in mechanism to enable both implantation and long-term retrieval of the LP.
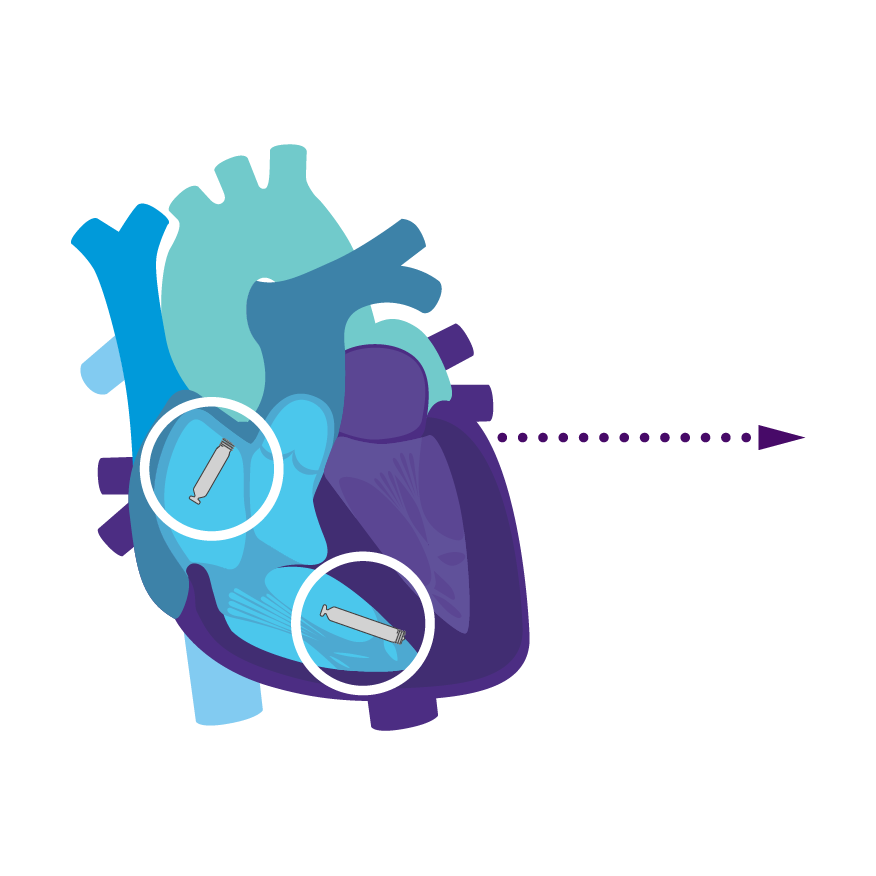
Mapping Prior to Fixation
AVEIR VR and AVEIR AR2 LPs can measure R/P-waves, impedance and Current of Injury via commanded EGM, and an initial capture threshold before fixation by simply touching the electrode to the endocardial tissue.2 The LPs are engaged with a rotational motion in the endocardium, and mapping capability is designed to help reduce the number of repositioning attempts.2
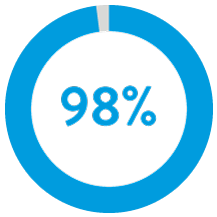
98% of patients had successful ventricular implants with 1 or less repositioning attempts.5
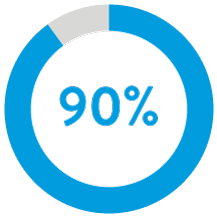
90% of patients had successful atrial implants with 1 or less repositioning attempts.5
Stay Informed
Sign up to hear about our technology, education opportunities, and more.
Read the Latest Blog Article
Stay up to date with recent news, product highlights, and case studies.
References
- Ip, J., Brady, P., et al. (2024, May 16-19). Leadless vs. Transvenous Single-Chamber Ventricular Pacemakers: Real-World Evidence from Aveir™ VR Coverage with Evidence Development (CED) Study [Poster Presentation]. HRS 2024, Boston, MA, United States. Poster Session III-1715873549040.pdf (heartrhythmjournal.com)
- AVEIR Leadless Pacemakers and Delivery Catheter IFU. ARTEN600361108.
- Abbott. Data on file, Supplemental Longevity Assessments of AVEIR DR System. Item: 91101444
- Neuzil, Petr, et al. “Worldwide Chronic Retrieval Experience of Helix-Fixation Leadless Cardiac Pacemakers.” Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 2025.
- Knops, Reinoud E., et al. "A Dual-Chamber Leadless Pacemaker." New England Journal of Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2300080
MAT-2306873 v8.0
.png)