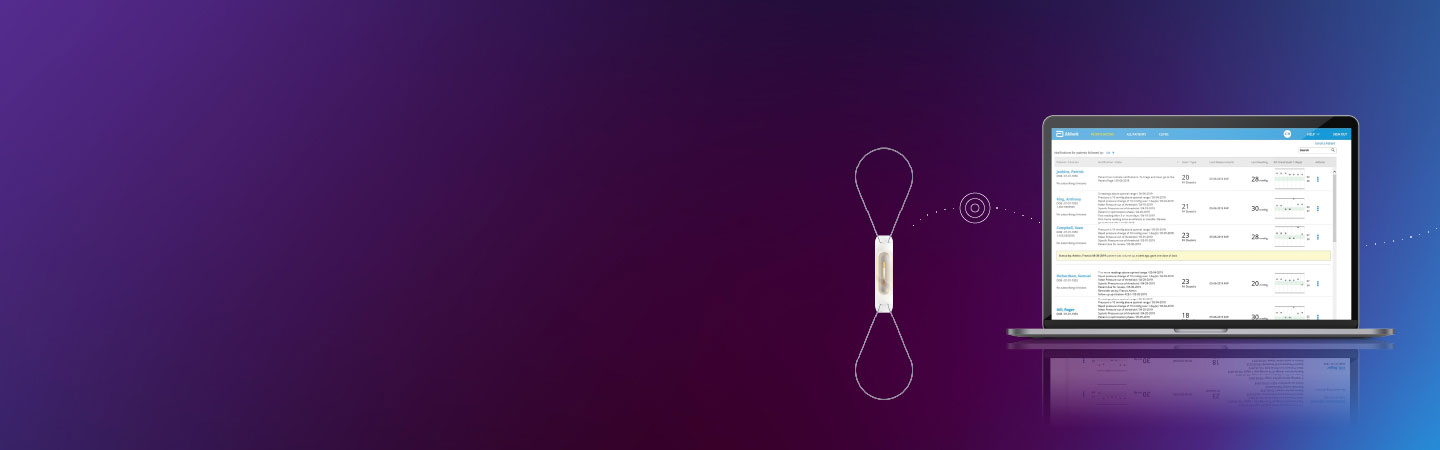
About the CardioMEMS HF System
The CardioMEMS™ HF System allows clinicians to monitor heart failure patients’ pulmonary artery (PA) pressure for proactive and actionable heart failure (HF) management and treatment. With early indications of worsening heart failure, you can make treatment adjustments remotely to optimize guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) and help slow the progression of heart failure,1 often before patients feel symptoms.
Abbott’s CardioMEMS HF System is the leading remote monitoring platform for both HFpEF2 and HFrEF patients clinically proven to:
- Aid physicians in preventing worsening heart failure3
- Lower heart failure mortality rates4
- Improve quality of life for heart failure patients5
Indications
The CardioMEMS HF System is indicated for wirelessly measuring and monitoring pulmonary artery pressure and heart rate in NYHA Class II or III heart failure patients who either have been hospitalized for heart failure in the previous year and/or have elevated natriuretic peptides. The hemodynamic data are used by physicians for heart failure management with the goal of controlling pulmonary artery pressures and reducing heart failure hospitalizations.
Contraindications
The CardioMEMS HF System is contraindicated for patients with an inability to take dual antiplatelet or anticoagulants for one month post implant.
CardioMEMS HF System Clinical Evidence
Multiple clinical trials have evaluated the safety and effectiveness of the CardioMEMS HF System. For a deep dive into the clinical studies and trial designs, visit Clinical Evidence and Journal Article information.
Key Clinical Outcomes
Improved Survival6-7

Reduction in Heart Failure Hospitalizations for HFpEF and HFrEF Patients8
Outstanding Safety Data

For the full resource list, visit Reimbursement & Coding for the CardioMEMS HF System.
References
- Brugts, J et al. Remote haemodynamic monitoring of pulmonary artery pressures in patients with chronic heart failure (MONITOR-HF): a randomised clinical trial. The Lancet. May 20, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00923-6
- Adamson PB, Abraham WT, Bourge RC, Costanzo MR, Hasan A, Yadav C, et al. Wireless pulmonary artery pressure monitoring guides management to reduce decompensation in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circulation: Heart Failure. 2014;7(6):935-944.
- Adamson PB. Pathophysiology of the transition from chronic compensated and acute decompensated heart failure: new insights from continuous monitoring devices. Current Heart Failure Reports. 2009;6:287-292.
- Abraham J, et al. Association of Ambulatory Hemodynamic Monitoring with Clinical Outcomes in a Concurrent Matched Cohort Analysis. JAMA Cardiology. 2019;4(6):556-563.
- Abraham WT, Stevenson LW, Bourge RC, Lindenfeld JA, Bauman JG, Adamson PB, for the CHAMPION Trial Study Group. Sustained efficacy of pulmonary artery pressure to guide adjustment of chronic heart failure therapy: complete follow-up results from the CHAMPION randomised trial. The Lancet. 2016;387(10017):453-461.
- Givertz MM, Stevenson LW, Costanzo MR, Bourge RC, Bauman JG, Ginn G, Abraham WT; CHAMPION Trial Investigators. Pulmonary Artery Pressure-Guided Management of Patients With Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017.
- JoAnn Lindenfeld, on behalf of the GUIDE-HF, CHAMPION, and LAPTOPHF investigators. Longer Term Effects of Hemodynamic Monitoring on Outcomes: A Combined Data Analysis of patients with HFrEF in CHAMPION, GUIDE-HF, and LAPTOP-HF. Presented at THT Conference, Boston, MA, March 2023.
- Shavelle D. et al. Lower rates of heart failure and all-cause hospitalizations during pulmonary artery pressure-guided therapy for ambulatory heart failure. Circulation: Heart Failure. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1161/circheartfailure.119.006863.
MAT-2006904 v7.0