Experience the OCT difference.
Request your Abbott Sales rep today.
OCT-guided PCI Improved Procedural Outcomes and Safety Results compared to Angiography-Guided PCI as Demonstrated in ILUMIEN IV1, OCTOBER2
ILUMIEN IV
ILUMIEN IV is the largest global imaging randomized clinical trial with n=2,487 patients in 80 global centers. The trial compared OCT-guided stent implantation vs. angiography guided in high-risk or complex lesions. Primary endpoint was achieving larger post-PCI lumen dimensions and improving clinical outcomes.
ILUMIEN IV OVERVIEW

KEY RESULTS:
OCT-guided PCI significantly reduced stent thrombosis (ST) by 64%

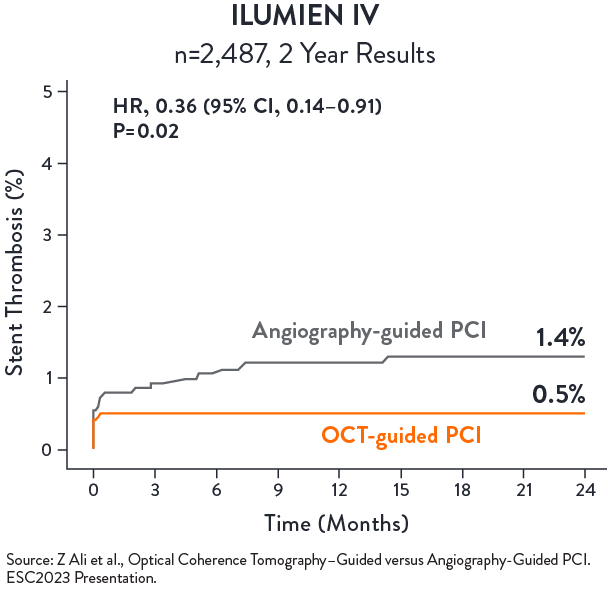
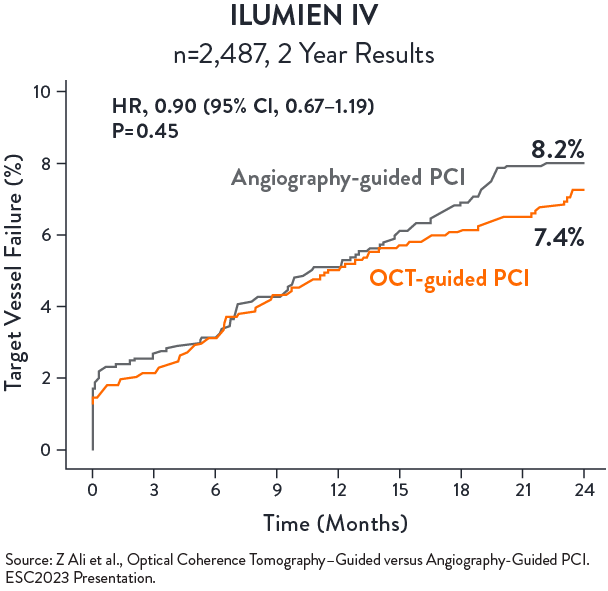
No statistical difference in TVF between OCT-guided and angio-guided PCI at 2 years
ILUMIEN IV SUBSTUDY: COMPLEX LESIONS3
ILUMIEN IV Substudy: Complex Lesions aimed to specifically examine if OCT-guided PCI improves procedural and clinical outcomes compared with angio-guided PCI outcomes in the complex angiographic lesions subgroup (N=1,973)
KEY RESULTS:
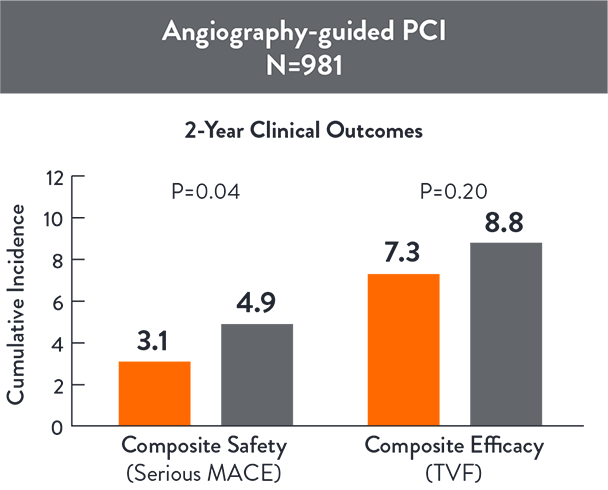
OCT-guided PCI reduced serious MACE (Cardiac Death, TV-MI, or Stent Thrombosis) compared with angio-guided PCI at 2 years (p=0.042)3

Source: Ali Z., et al. ILUMIEN IV: OCT-guided vs. angio-guided coronary stent implantation in complex lesions (Sub-group). EuroPCR2024.
Source: Ali Z., et al. ILUMIEN IV: OCT-guided vs. angio-guided coronary stent implantation in complex lesions (Sub-group). EuroPCR2024.
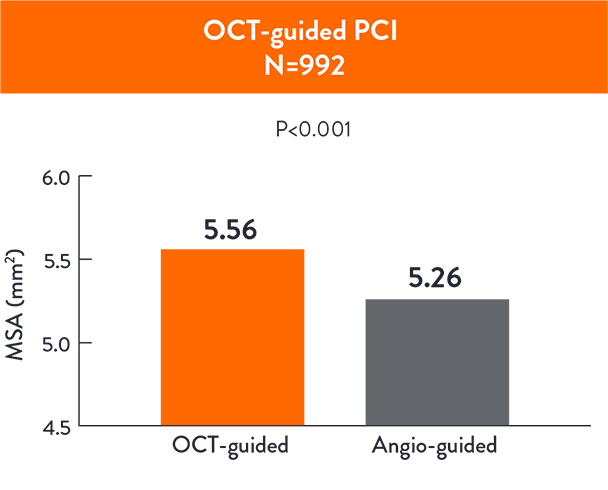
OCT-guided PCI led to a larger MSA ( 5.56 ± 1.95 mm 5.26 ± 1.81 mm2; p< 0.001) compared to angio-guided PCI3

CALIPSO3
CALIPSO Trail (Calcified Lesion Intervention Planning Steered by OCT) is the first controlled randomized trial (n=134) that compared OCT-guided PCI to angio-guided PCI in moderate to severe calcified lesions using pre-defined algorithm for plaque modification, stent sizing and optimization.
- Primary endpoint: post-PCI Minimal Stent Area (MSA) on final OCT
- Secondary endpoints: Efficiency and Safety
KEY RESULTS:
OCT-guided PCI was superior to angio-guided PCI with greater MSA 6.5 (5.5-8.1) vs. 5.0 (4.1-6.1) mm2, p<0.0014.

OCT-guided PCI achieved greater stent expansion and lower malapposition than angio-guided PCI4
| OCT guidance group (n=65) | Angio guidance group (n=69) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stent length, mm | 33.0 (24.0-48.0) | 38.0 (25.0-48.0) | 0.35 |
| Average stent area, mm2 | 8.4 (7.0-10.3) | 7.4 (6.4-8.6) | 0.01 |
| Successful geometrical expansion, n (%) | 49 (75) | 20 (29) | <0.001 |
| Major malapposition, n (%) | 23 (35) | 34 (49) | 0.10 |
| Malapposition maximal distance, µm | 535 (352-700) | 570 (330-790) | 0.13 |
| Major malapposition length, mm | 0 (0-2) | 0 (0-4) | 0.03 |
| Malapposed stent percentage, % | 0 (0-8.3) | 0 (0-14.5) | 0.02 |
| Average stent eccentricity | 1.21 (1.16-1.25) | 1.19 (1.17-1.24) | 0.87 |
| Maximal stent eccentricity | 1.43 (1.35-1.55) | 1.51 (1.36-1.60) | 0.47 |
| Major dissection, n (%) | 7 (11) | 13 (19) | 0.19 |
Source: Amabile N., et al. OCT vs. angiography for guidance of calcified lesions PCI: the CALIPSO (CAlcified Lesion Intervention Planning Steered by OCT) trial. EuroPCR2024.
No difference in contrast use, procedure time & radiation dose between OCT-guided and angio-guided PCI4
| OCT guidance group (n=65) | Angio guidance group (n=69) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Procedure duration, mins | 63 (51-87) | 64 (46-82) | 0.22 |
| Fluoroscopy duration, mins | 17 (11-21) | 17 (12-27) | 0.95 |
| Total X ray dose, cGy/cm2 | 4148 (2550-7155) | 4403 (2630-7333) | 0.65 |
| Contrast medium volume, ml | 180 (140-233) | 184 (150-219) | 0.88 |
Source: Adapted from Amabile N., et al. OCT vs. angiography for guidance of calcified lesions PCI: the CALIPSO (CAlcified Lesion Intervention Planning Steered by OCT) trial. EuroPCR2024.
DOCTORS-LM5
DOCTORS LM is a randomized open label trial to assess if OCT-guided PCI of the Left Main is superior to angio-guided PCI of the Left Main, assessed by Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR)
- Primary endpoint: FFR value measured at the end of the procedure in the main vessel
- Secondary endpoints:
- Proportion of patients with optimal post-PCI FFR (≥90)
- Minimal Stent Area
- Procedural Success (optimal stent deployment, absence of malapposition, edge dissection or crushed stent)
- MACE at 1 year
KEY RESULTS:
OCT-guided PCI showed similar functional outcomes in left main lesions compared to angio-guided PCI5
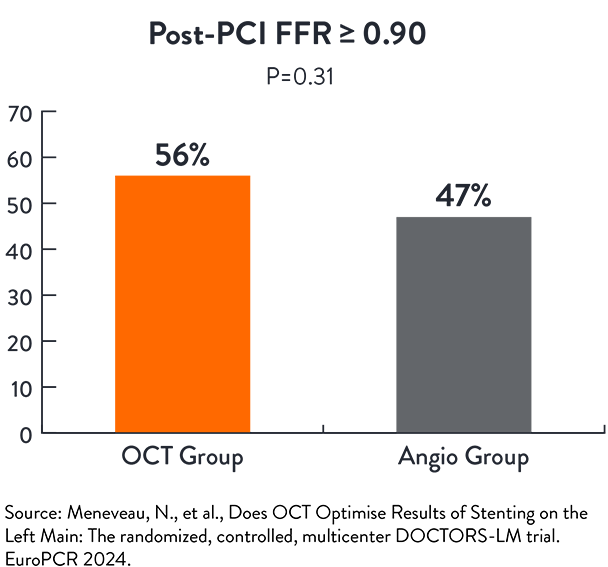
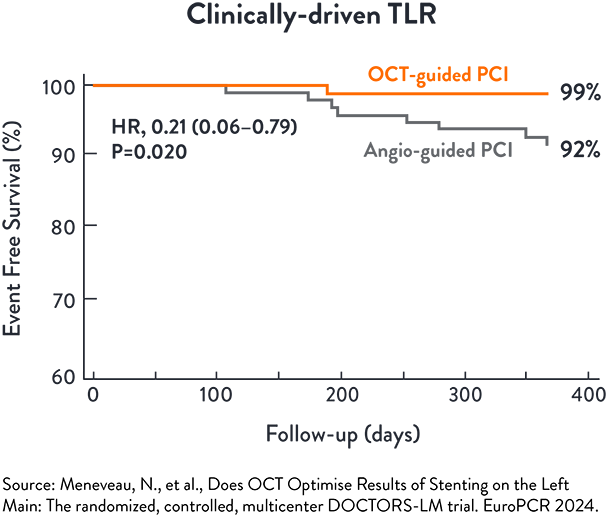
The incidence of TLR at 1 year was significantly lower in the OCT-guided PCI (p=0.020) than angio-guided PCI5

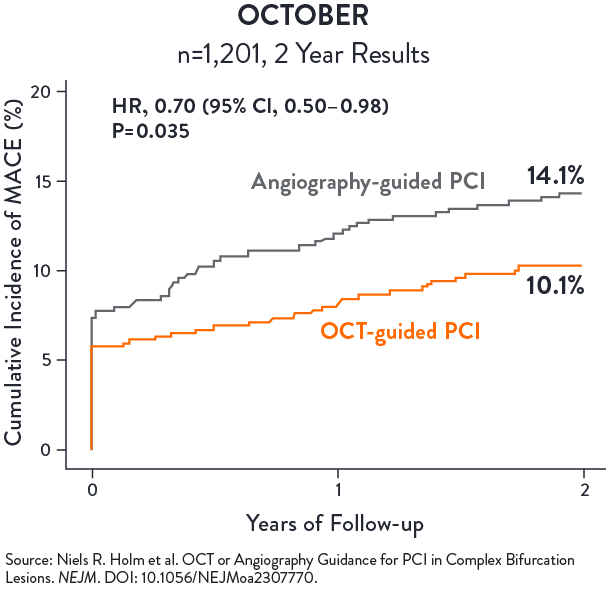
OCTOBER
OCTOBER trial was conducted in 38 heart centres across 13 European countries with n=1,201 patients randomized in a 1:1 ratio to undergo OCT-guided or angiography-guided PCI of bifurcation coronary lesions. A step-wise protocol was use in the OCT arm; in the angiography arm, intravascular ultrasound use was discouraged but could be pursued for left main (LM) PCI.
The primary endpoint was major adverse cardiac events (MACE), defined as a composite of cardiac death, target lesion myocardial infarction (TL-MI), and ischemia-driven target lesion revascularization (ID TLR), after two years.
KEY RESULTS:
OCT-guided PCI of complex bifurcation lesions is superior to angiography-guided PCI for major adverse cardiac events at 2 years2
- MACE @ 2 years:
(10.1% vs 14.1%, p=0.035) - Cardiac death:
1.4% vs. 2.6% (HR 0.53, 95% CI 0.22–1.25) - ID TLR:
2.8% vs. 4.6% (HR 0.60, 95% CI 0.32–1.13) - TL-MI:
7.8% vs. 8.5% (HR 0.90, 95% CI 0.60–1.34)
From Evidence to Practice: A Pragmatic Approach to OCT.
Watch Dr. Johnson demonstrate how to apply OCT-guidance to a complex bifurcation case from a participant in the OCTOBER Trial with a highly challenging left main stent.
Additional body of evidence in support of OCT-guided PCI
Multiple other studies of OCT-guided PCI vs. angiography alone suggest that intravascular imaging with OCT is associated with better clinical performance6,8,10
| STUDY | SIZE | OUTCOMES |
|---|---|---|
| CLI-OPCI I (EuroIntervention, 2012) | 335 pts OCT guided vs 335 pts angio-guided | Reduced rate of cardiac death and MACE in patients who underwent OCT-guided stent intervention.6 |
| ILUMIEN I (EHJ, 2015) | 418 pts | OCT imaging influenced physician decision-making pre-PCI in 57% and post-PCI in 27% of all cases.7 |
| ILUMIEN III (LANCET, 2016) | 450 pts (158 OCT, 146 IVUS, 146 ANGIO) | OCT- guided PCI resulted in superior stent expansion and procedural success compared to angiography-guided PCI.8 |
| DOCTORS (CIRC 2016) | 240 pts NSTEMI | In patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary sydromes, OCT-guided PCI is associated with higher post-procedure FFR than angio-guided PCI.9 |
| PAN-LONDON (JACC CARD INT, 2018) | 1,149 pts OCT, 10,971 pts IVUS 75,046 pts angio | OCT-guided PCI was associated with improved procedural outcomes, in-hospital events and long term survival compared with standard angiography-guided PCI.10 |
References
- Ali Z. et al., Optical Coherence Tomography–Guided versus Angiography-Guided PCI, NEJM, DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa230586
- Holm N.R. et al., OCT or Angiography Guidance for PCI in Complex Bifurcation Lesions, NEJM, DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2307770 (OCTOBER)
- Ali Z., et al. ILUMIEN IV: OCT-guided vs. angio-guided coronary stent implantation in complex lesions (Sub-group). EuroPCR2024.
- Amabile N., et all. OCT vs angiography for guidance of calcified lesions PCI: the CALIPSO trial. EuroPCR 2024
- Meneveau N et al. Does OCT Optimise Results of Stenting on the Left Main: The randomized, controlled, multicentre DOCTORS-LM trial. EuroPCR 2024.
- Prati F. et al. Angiography alone versus angiography plus optical coherence tomography to guide decision-making during percutaneous coronary intervention: (CLI-OPCI) study. EuroIntervention, 2012.
- Wijns W. et al. Optical coherence tomography imaging during percutaneous coronary intervention impacts physician decision-making: ILUMIEN I study. European Heart Journal (2015) 36, 3346–3355 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehv367.
- Z. Ali et al. Optical coherence tomography compared with intravascular ultrasound and with angiography to guide coronary stent implantation (ILUMIEN III: OPTIMIZE PCI): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31922-5.
- Menevue N. et al. Optical Coherence Tomography to Optimize Results of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients with Non–ST-Elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome DOCTORS: https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.024393 Circulation. 2016;134:906–917.
- Jones, D. et al. Angiography Alone Versus Angiography Plus Optical Coherence Tomography to Guide Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Outcomes From the Pan-London PCI CohortPan London: JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2018 Jul 23;11(14):1313-1321. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2018.01.274.
MAT-2310265 v3.0
