Welcome to the forefront of cardiac care with the Navitor TAVI System. Our commitment to innovation, patient safety, and clinical excellence makes us the preferred choice for transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI*) procedures worldwide. The Navitor TAVI System offers stable delivery, remarkable performance, and is future ready.
Stable delivery.
- The confidence of controlled deployment.
- Largest valve. Smallest delivery system to date.2
- Three large and highly visible radiopaque markers.
Remarkable performance.1
- 0% Moderate to Severe PVL†
- 2.0 cm² Effective Orifice Area†
- 7.4 mmHg Mean Gradient†
- 1.9% All-Cause Mortality
- 1.9% Disabling Stroke
- 3.8% Life-Threatening Bleeding
- 1.9% Acute Kidney Injury Stage 2/3
- 4.2% Major Vascular Complications
Future ready.
- Uncompromised coronary access
- Future ready index valve

Ordering Information
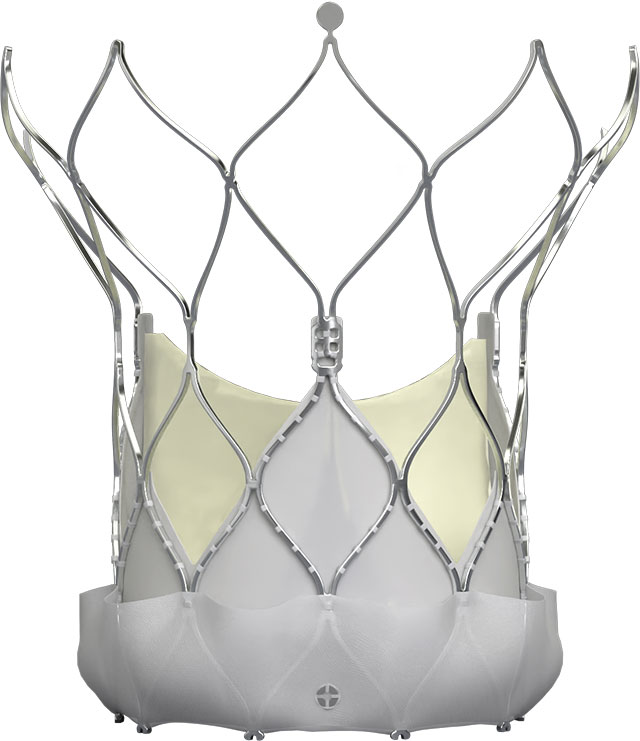
Navitor™ Transcatheter Aortic Valve
| Catalog Number | Valve Size (mm) | Annulus Use Range Diameter (mm)6 | Annulus Area (mm²)6 | Annulus Perimeter (mm)6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NVRO-23 | 23 | 19-21 | 277–346 | 60–66 |
| NVRO-25 | 25 | 21–23 | 338–415 | 66–73 |
| NVRO-27 | 27 | 23–25 | 405–491 | 72–79 |
| NVRO-29 | 29 | 25–27 | 479–573 | 79–85 |
| NVRO-35 | 35 | 27–30 | 559–707 | 85–95 |
FlexNav™ Delivery System
| Catalog Number | Equivalent Integrated Sheath Diameter (F)6 | Valve Capsule Outer Diameter (mm)6 | Integrated Sheath Working Length (cm)6 | Delivery System Working Length (cm)6 | Minimum Vessel Diameter Requirement (mm)6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FNAV-DS-SM | 14 | 6.0 | 30 | 107 | ≥ 5.0 |
| FNAV-DS-LG | 15 | 6.3 | 30 | 107 | ≥ 5.5 |
Navitor™ Loading System
| Catalog Number | |
|---|---|
| NVTR-LS-SM | The Navitor™ loading system facilitates valve preparation/loading onto the FlexNav™ delivery system. The loading system includes a loading funnel, loading base, base insert, loading tube, stent guide and leaflet tester. The SM and LG+ loading systems contain base inserts to facilitate loading the Navitor valve according to the labeled size on the base insert. In addition, the base insert and loading tube are color-coded to differentiate between the different configurations. |
| NVTR-LS-LG+ |
* Also referred to as TAVR (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement)
† 30-Day Echo Core Lab Data
References
- Navitor™ TAVI System IFU.
- Abbott data on file 90734545/90465559.
Rx Only
Important Safety Information
NAVITORTM TRANSCATHETER AORTIC VALVE IMPLANTATION SYSTEM
Indications
The Navitor™ Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation System is indicated for relief of aortic stenosis in patients with symptomatic heart disease due to severe native calcific aortic stenosis who are judged by a heart team, including a cardiac surgeon, to be high or greater risk for open surgical therapy (i.e., predicted risk of surgical mortality ≥ 8% at 30 days, based on the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) risk score and other clinical comorbidities unmeasured by the STS risk calculator).
Contraindications
The valve is contraindicated for patients with inability to tolerate antiplatelet/anticoagulant therapy or nitinol alloy (nickel and titanium), or who have active infections, including endocarditis.
Potential Adverse Events
Adverse events potentially associated with the use of transcatheter bioprosthetic heart valves include but are not limited to: access site complications (e.g., pain, bleeding, infection, hematoma, pseudoaneurysm, etc.); acute coronary obstruction; acute myocardial infarction; allergic reaction to antiplatelet agents, contrast medium, or valve components; aortic rupture; ascending aorta trauma; atrio-ventricular node block; cardiac arrhythmias; conduction system injury; conversion to open surgical procedure; death; dissection; embolism; emergent balloon valvuloplasty; emergent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI); emergent surgery (i.e., coronary artery bypass, heart valve replacement); endocarditis; explantation; heart failure; hemodynamic compromise; hemolysis; hemolytic anemia; hemorrhage; hypotension or hypertension; infection; myocardial ischemia; mitral valve insufficiency; multi-organ failure; non-structural dysfunction (i.e., entrapment by pannus, paravalvular leak, inappropriate sizing or positioning); pannus; pericardial effusion; perforation of the myocardium, ventricle, or a blood vessel; permanent disability; permanent pacemaker; regurgitation; renal insufficiency or renal failure; reoperation; respiratory failure; sepsis; stroke; structural deterioration (i.e., calcification, leaflet tear); thrombosis; tamponade; transfusion; valve embolization or migration; vessel dissection or spasm.
MAT-2300253 v2.0
