Welcome to the forefront of cardiac care with the Navitor TAVI System. Our commitment to innovation, patient safety, and clinical excellence makes us the preferred choice for transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI*) procedures worldwide. The Navitor TAVI System offers stable delivery, remarkable performance, and is future ready.
Stable delivery.
- The confidence of controlled deployment.
- Largest valve. Smallest delivery system to date.1
- Three large and highly visible radiopaque markers.
Remarkable performance.2
- 0% Moderate to Severe PVL†
- 2.0 cm² Effective Orifice Area†
- 7.4 mmHg Mean Gradient†
- 1.9% All-Cause Mortality
- 1.9% Disabling Stroke
- 3.8% Life-Threatening Bleeding
- 1.9% Acute Kidney Injury Stage 2/3
- 4.2% Major Vascular Complications
Future ready.
- Uncompromised coronary access
- Future ready index valve

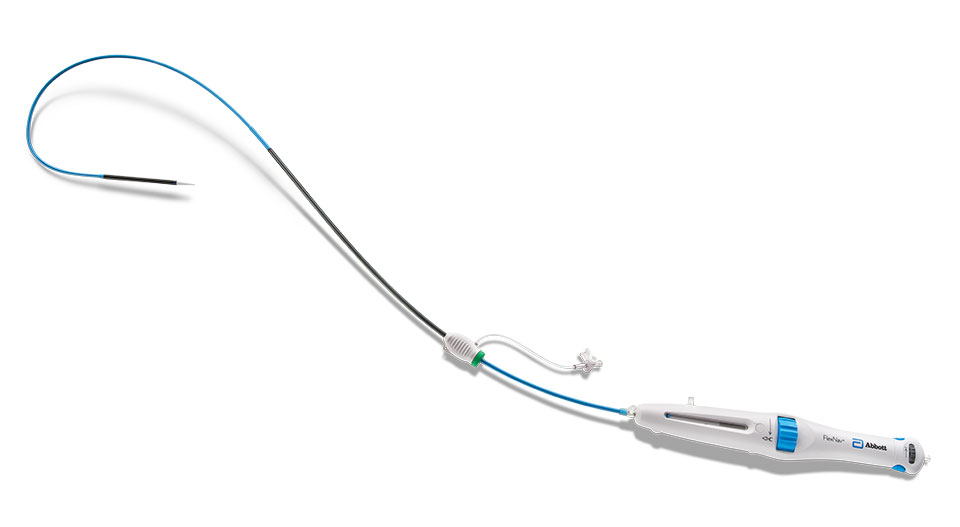
Ordering Information
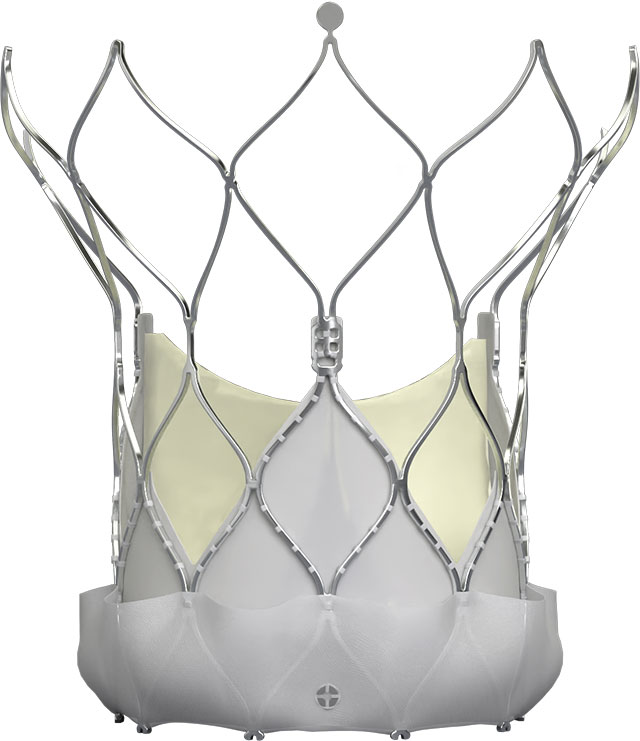
Navitor™ Transcatheter Aortic Valve
| Catalog Number | Valve Size (mm) | Annulus Use Range Diameter (mm)2 | Annulus Area (mm²)2 | Annulus Perimeter (mm)2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NVRO-23 | 23 | 19-21 | 277–346 | 60–66 |
| NVRO-25 | 25 | 21–23 | 338–415 | 66–73 |
| NVRO-27 | 27 | 23–25 | 405–491 | 72–79 |
| NVRO-29 | 29 | 25–27 | 479–573 | 79–85 |
| NVRO-35 | 35 | 27–30 | 559–707 | 85–95 |
FlexNav™ Delivery System
| Catalog Number | Equivalent Integrated Sheath Diameter (F)2 | Valve Capsule Outer Diameter (mm)2 | Integrated Sheath Working Length (cm)2 | Delivery System Working Length (cm)2 | Minimum Vessel Diameter Requirement (mm)2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FNAV-DS-SM | 14 | 6.0 | 30 | 107 | ≥ 5.0 |
| FNAV-DS-LG | 15 | 6.3 | 30 | 107 | ≥ 5.5 |
Navitor™ Loading System
| Catalog Number | |
|---|---|
| NVTR-LS-SM | The Navitor™ loading system facilitates valve preparation/loading onto the FlexNav™ delivery system. The loading system includes a loading funnel, loading base, base insert, loading tube, stent guide and leaflet tester. The SM and LG+ loading systems contain base inserts to facilitate loading the Navitor valve according to the labeled size on the base insert. In addition, the base insert and loading tube are color-coded to differentiate between the different configurations. |
| NVTR-LS-LG+ |
* Also referred to as TAVR (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement)
† 30-Day Echo Core Lab Data
References
- Abbott data on file 90734545/90465559.
- Navitor™ TAVI System IFU.
MAT-2409501 v1.0
