Reduce the long-term dangers of radiation exposure and orthopedic injuries caused by fluoroscopy by adopting the world’s most widely used and published solution for intracardiac echo, transseptal access, and ablation support1 in a low-fluoro workflow.
Reduce Fluoro
Exposure
Reduce
Procedure Time
Improve Case
Margins
Reduce Fluoro Exposure
By an average of
6.95 minutes2
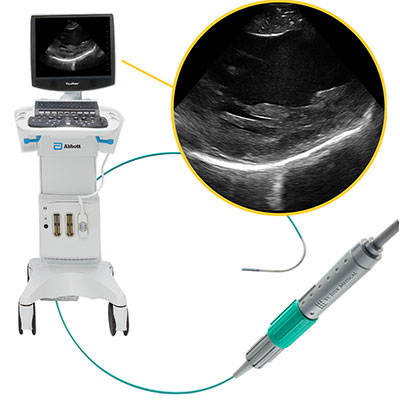
through ICE-guided ablation using ViewFlex™ Xtra ICE Catheter

By 27%
(33 min vs 45 min)3 with Agilis™ NxT Steerable Introducer

Reduce Procedure Time
By an average of
15.2 minutes2
through ICE-guided ablation using ViewFlex™ Xtra ICE Catheter

By 32%
(30.4 min vs 44.6 min)4 with Agilis™ NxT Steerable Introducer

Improve Case Margins
Enable efficient and economical access capitalizing on the competitive price offered with the combined use of ViewFlex Xtra ICE Catheter, Agilis NxT Steerable Introducer, and BRK™ Transseptal Needle, XS Series

Reduce Radiation: The Complete Low-Fluoro Solution
ViewMate™ Ultrasound Console & ViewFlex™ Xtra ICE Catheter
421,000+
procedures worldwide1
Offers enhanced resolution with outstanding image quality

Reduce complications with ICE-guided ablation

Cardiac Complications6
Such as pericardial effucsion, tamponade, thrombus formation, pulmonary vein stenosis, with microbubbles detected as a result of overheating.2

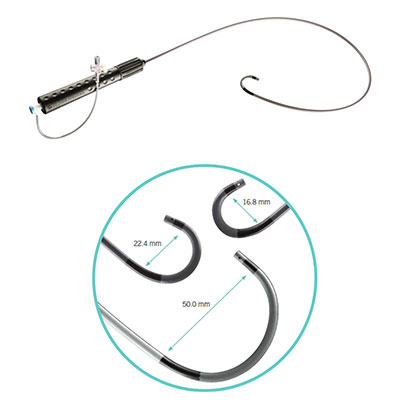
Agilis™ NXT Steerable Introducer
1,600,000+
procedures worldwide1
Choose the Gold Standard
Tailor to your patient’s anatomy with a large variety of sizes & curves that maintain their shape.

Confident Steering and Stable Positioning with Exceptional Maneuverability
Access hard-to-reach areas with precise maneuverability and auto-lock steering, such as the right inferior and left anterior pulmonary veins7

Reliable, Complete Lesion Creation Through Outstanding Agility and Stability

Greater Freedom from Arrhythmia at 6 Months
(76.0% vs 53.0%)3 and 18% greater at 12 months (74.0% vs 62.7%)8

BRK™ Transseptal Needle, XS Series

2,600,000+
procedures worldwide1
Go Transseptal Efficiently and Economically
Experience the consistency, reliability and flexibility of the world’s most widely used1 transseptal needle design

Proven Performance in Varied Anatomies
- A steeper angle of approach with two curve styles: the standard BRK Transseptal Needle, XS Series curve or the BRK-1™ Transseptal Needles, XS Series curve
- Procedural accuracy with three usable lengths: 71cm, 89cm, 98cm

Watch a Low-Fluoro Case and Workflow
View Dr. Arjun Gururaj, MD as he utilizes ViewFlex™ Xtra ICE Catheter, in conjunction with the EnSite Precision™ Cardiac Mapping System, to minimize fluoro usage in this re-do AF Ablation case. Dr. Gururaj performs a double-transseptal under ICE guidance, while highlighting various structures and views to assist in a low-fluoro workflow throughout the case.
Supported by Abbott: Your Single-Source EP Solution
The low-fluoro portfolio is integrated with Abbott’s leading electrophysiology solutions offering a broad range of product sizes, curves, and accessories to tailor to nearly any patient anatomy and clinician preference.
4.6+ Million
Utilizations1
Abbott's portfolio is the world's most widely used solution for intracardiac echo, transseptal access, and ablation support
Extensive
Clinical Data
Robust publications demonstrating proven patient outcomes, procedural efficiency, and accuracy
Important Safety Information
Agilis™ NxT Steerable Introducer
BRK™ Transseptal Needle, XS Series
ViewFlex™ Xtra ICE Catheter and ViewMate™ Ultrasound Console
References
- Abbott internal data on file PULSE data.
- Goya M, et al. The use of intracardiac echocardiography catheters in endocardial ablation of cardiac arrhythmia: Meta-analysis of efficiency, effectiveness, and safety outcomes. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2020;31:664–673.
- Piorkowski C, et al. (2011). Steerable versus non-steerable sheath technology in AF ablation: A prospective, randomized study. Circulation, 4(2), 157–165.
- Matsuo S, et al. (2010). Prospective randomized comparison of a steerable versus a non-steerable sheath for typical atrial flutter ablation. Europace, 12(3), 402–409.
- Casella M, et al. (2015). Near zero fluoroscopic exposure during catheter ablation of supraventricular arrhythmias: the NO-PARTY multicentre randomized trial. Europace (2016) 18, 1565–1572. doi:10.1093/europace/euv344
- Aldhoon B, et al. Complications of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in a high-volume centre with the use of intracardiac echocardiography. Europace (2013) 15, 24–32.
- Piorkowski C, et al. (2008). Steerable sheath catheter navigation for ablation of atrial fibrillation: A case-control study. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 31(7), 863–873.
- Mansour M. (2014). TOCCASTAR: Preliminary Results of the First Prospective Randomized Study of a Contact Force Sensing Ablation Catheter for the Treatment of Paroxysmal AF. Presented at HRS AF Summit 2014. San Francisco, California.
MAT-2214183 v3.0