Closure of Ventricular Septal Defects (VSD)
Ventricular septal defects are the most commonly found congenital heart defect.1 One subtype of these defects is the muscular VSD. If left untreated, it can lead to pulmonary hypertension and/or congestive heart failure.2 The Amplatzer™ Muscular VSD Occluders are designed for complete closure of these type of defects.
Quality Engineering
Device Features
- Device waist centers and closes the defect
- Symmetrical design allows a transcatheter femoral or arterial delivery approach
- Constructed from self-expanding Nitinol mesh and polyester material, which promotes tissue in-growth
- Precise placement through the device’s ability to be recaptured and redeployed
Amplatzer™ Muscular VSD Occluder
The Amplatzer™ Muscular VSD Occluder is intended for the closure of congenital ventricular septal defects in high-risk surgical patients. The 7 mm waist length is designed to accommodate the thickness of the muscular ventricular septal wall.
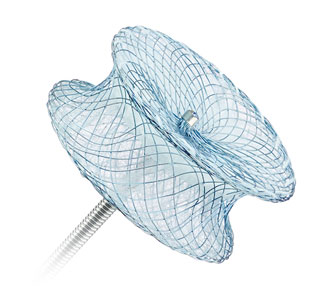
Amplatzer™ P.I. Muscular VSD Occluder
The Amplatzer™ P.I. Muscular VSD Occluder is intended for the closure of post myocardial infarction (P.I.) VSD. The 10 mm waist length is designed to accommodate the damaged muscular tissue of the septal wall following a myocardial infarction.

Designed for Optimal Occlusion
The Amplatzer Muscular VSD Occluder and Amplatzer P.I. Muscular VSD Occluder are self-expandable, double-disc devices made from a nitinol wire mesh and polyester material. The two discs are linked together by a connecting waist corresponding to the size of the VSD, providing optimal occlusion.
Ordering Information
AMPLATZER™ Muscular VSD Occluder
| Model/Reorder Number | Device Size/Waist Diameter (mm) | Disc Diameter (mm) | Waist Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9-VSD-MUSC-004 | 4 | 9 | 7 |
| 9-VSD-MUSC-006 | 6 | 14 | 7 |
| 9-VSD-MUSC-008 | 8 | 16 | 7 |
| 9-VSD-MUSC-010 | 10 | 18 | 7 |
| 9-VSD-MUSC-012 | 12 | 20 | 7 |
| 9-VSD-MUSC-014 | 14 | 22 | 7 |
| 9-VSD-MUSC-016 | 16 | 24 | 7 |
| 9-VSD-MUSC-018 | 18 | 26 | 7 |
AMPLATZER™ P.I. Muscular VSD Occluder
| Model/Reorder Number | Device Size/Waist Diameter (mm) | Disc Diameter (mm) | Waist Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9-VSDMPIHDE-016 | 16 | 26 | 10 |
| 9-VSDMPIHDE-018 | 18 | 28 | 10 |
| 9-VSDMPIHDE-020 | 20 | 30 | 10 |
| 9-VSDMPIHDE-022 | 22 | 32 | 10 |
| 9-VSDMPIHDE-024 | 24 | 34 | 10 |
References
- Hoffman J, Kaplan S. The incidence of congential heart disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2002;39(12):1890-1900
- Amplatzer Muscular VSD Occluder Instructions for Use.
MAT-2006713 v3.0