Right Energy, Right Time
with Precision Shock Technology
Gallant™ & Entrant™ ICDs & CRT-Ds
Gallant and Entrant ICDs & CRT-Ds
Timing is everything when shocking a patient out of VF. Precision Shock Technology delivers the right energy within the right time for greater first-shock success.1-9
Clinical data demonstrated patients programmed with optimized Precision Shock Technology significantly improved first-shock success by 14%.1

of first-shocks were successful with optimized Precision Shock Technology.1
*median % of shock success evaluated paired, intra-patient differences in shock success rate and delivered energy were evaluated.
Right Energy. Right Time. For greater first-shock success.1-5
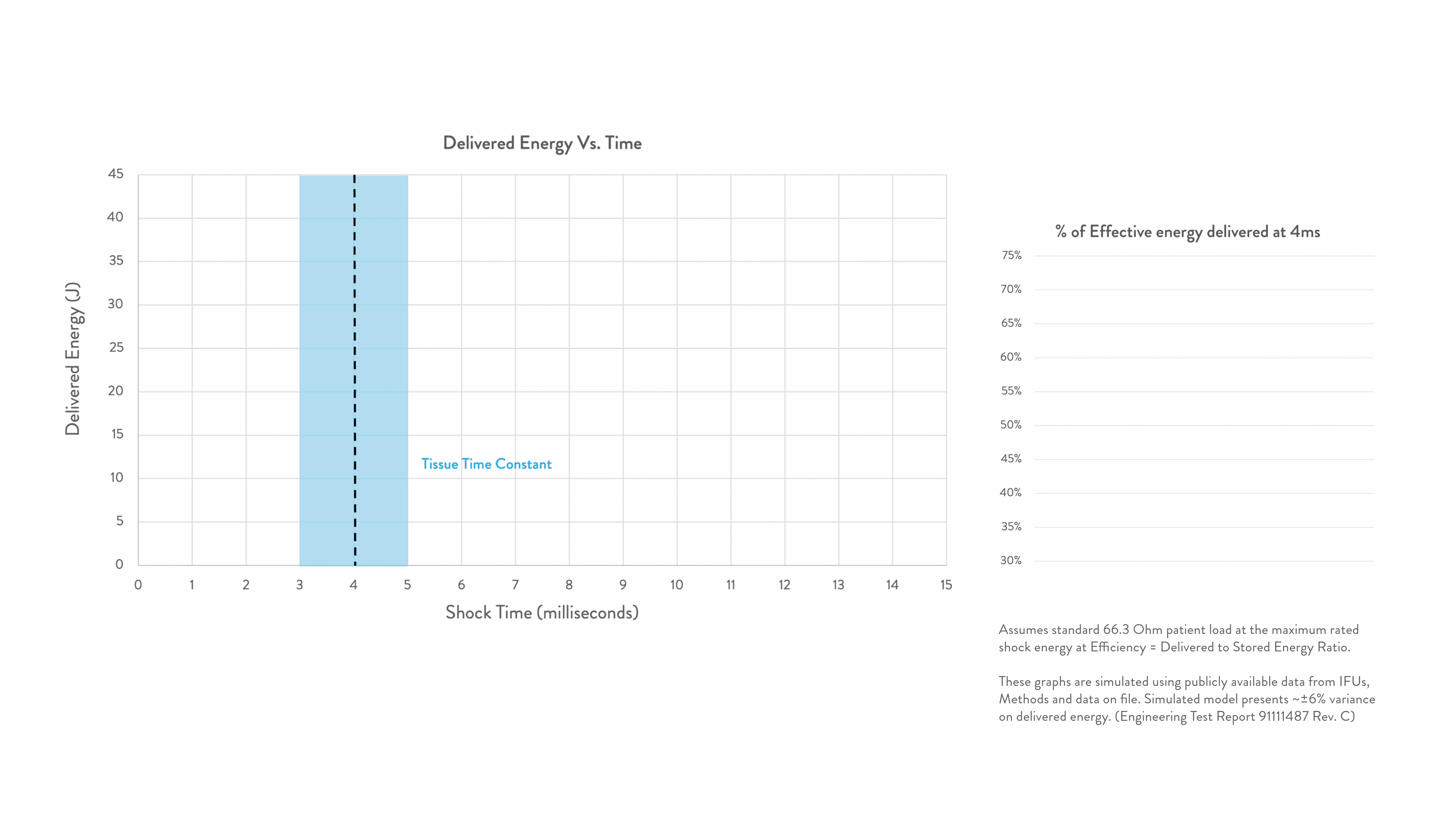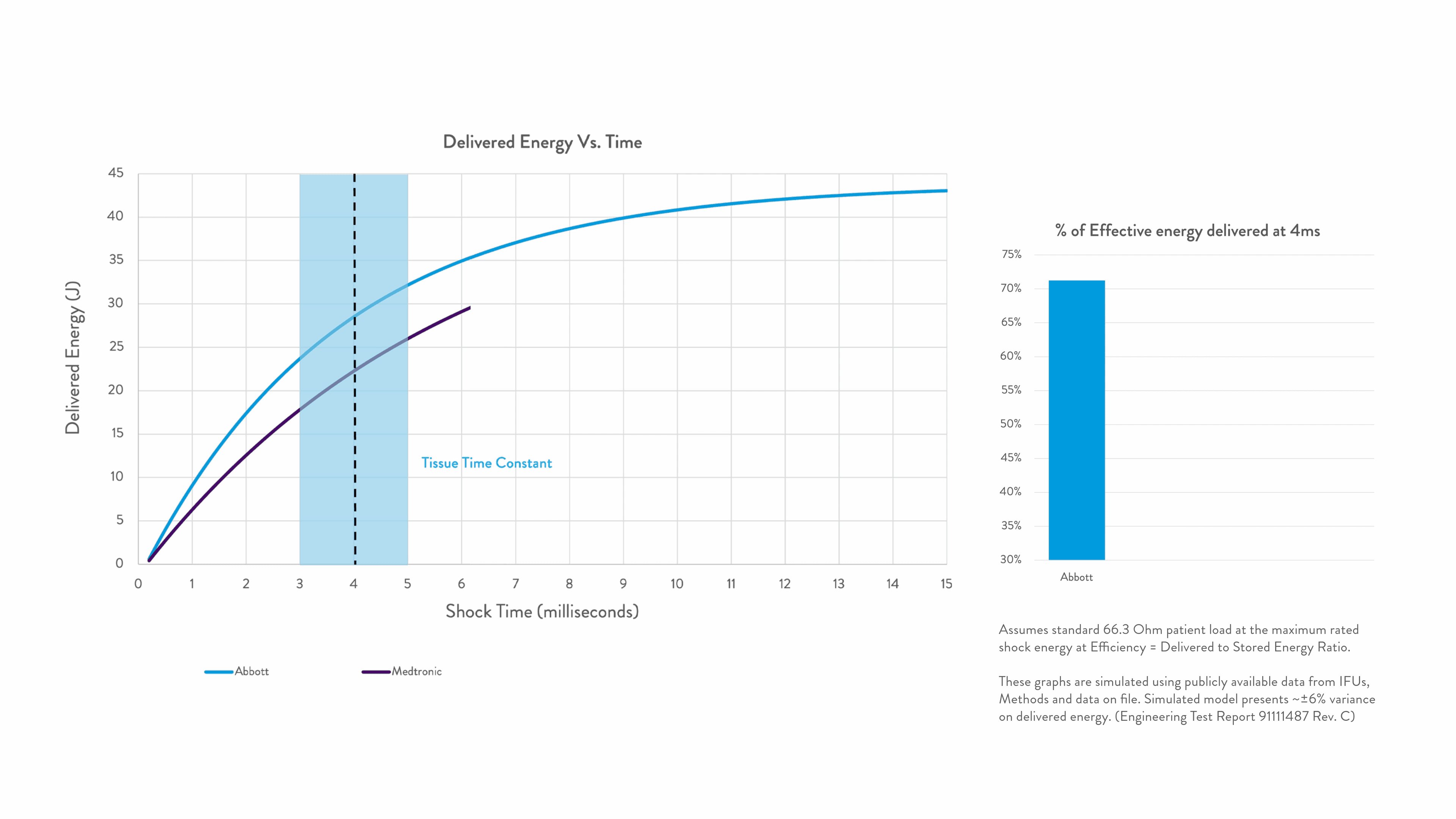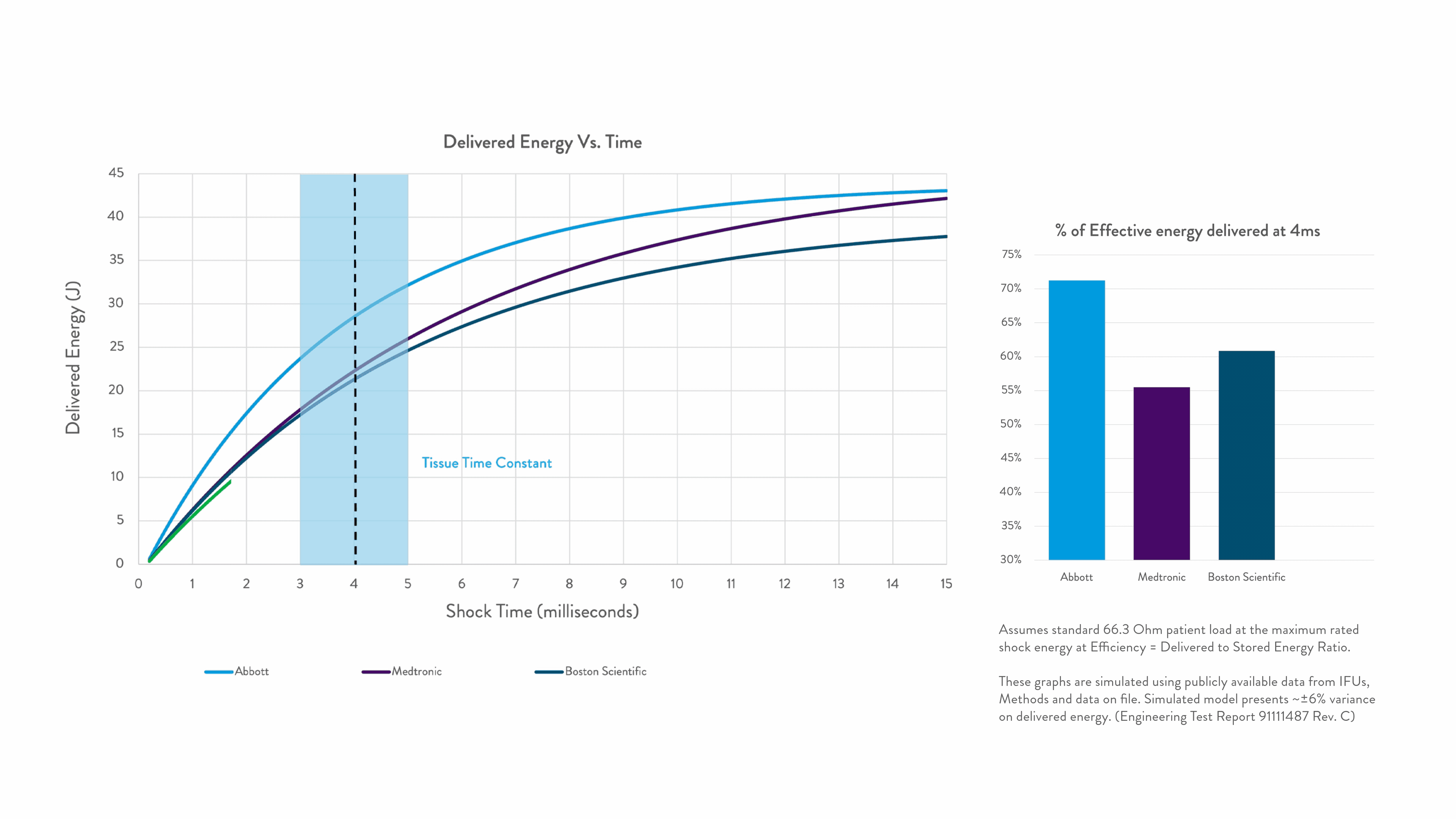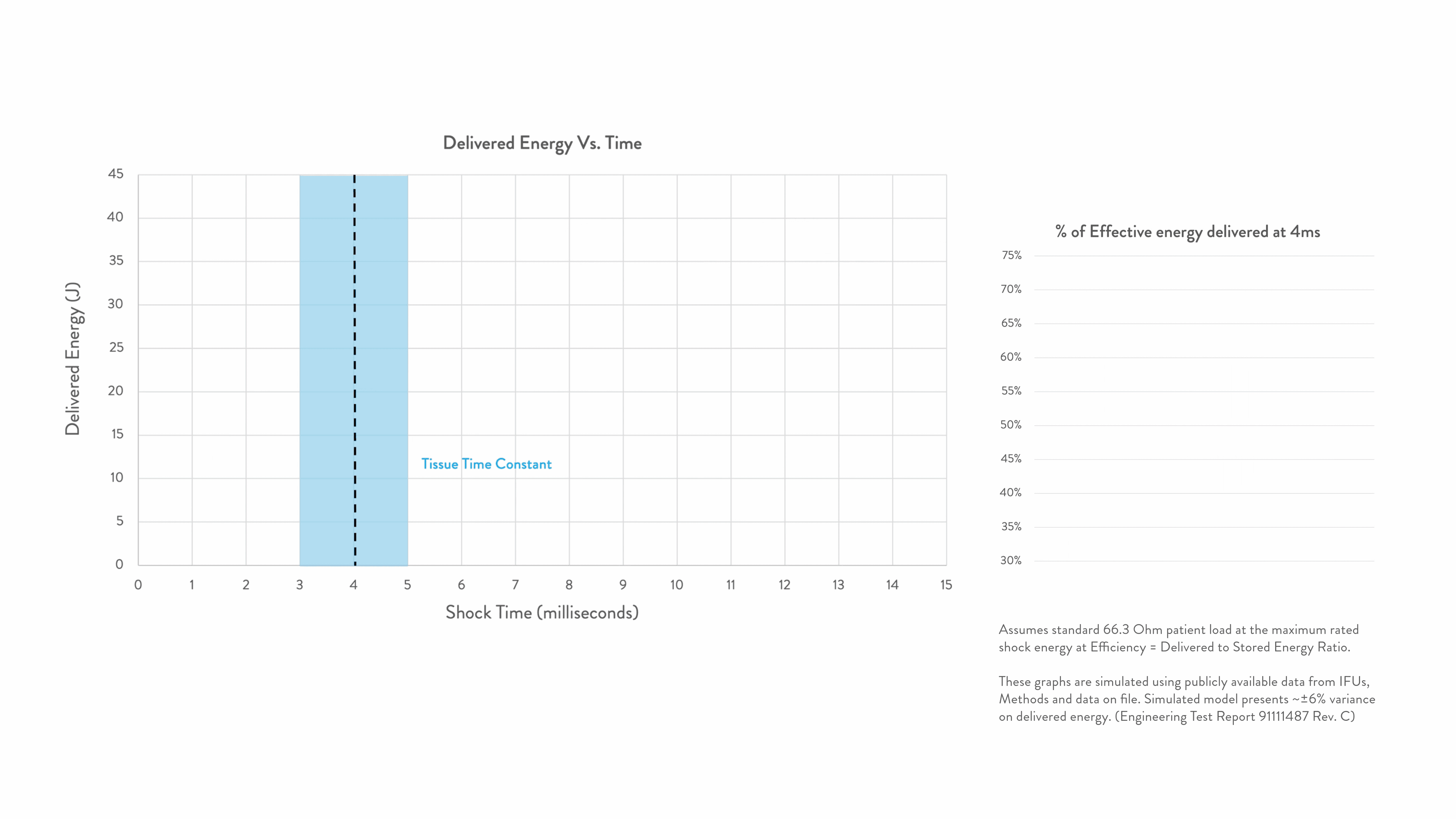
Energy delivered within the tissue time constant of 3-5 ms is the most effective for conversion.2-5
Any energy outside this response window is wasted.
Proven to provide narrower QRS and reduce heart failure hospitalizations.10, 11
SyncAVTM CRT Technology delivers nearly 2x the median acute QRSd improvement compared to off-the-shelf AV delays, regardless of pacing mode.10 HF hospitalization rates significantly reduce by 22% at 2 years with SyncAV CRT Technology ON vs OFF.11
.png)
BiV = BiV-pacing
MPP = MultiPoint pacing
LVSS = LV-only single site pacing
LVMPP = LV-only MultiPoint pacing
Real-World Clinical Evidence
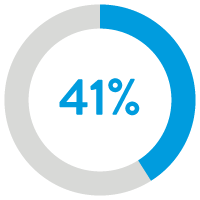
41% reduction in heart
failure readmissions12
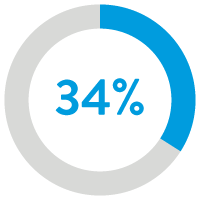
34% reduction in all-cause
hospitalization readmissions12
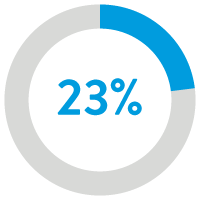
23% reduction ($1,135)
in 2-year cost12
$4,031
lifetime savings per
CRT patient12
Potential to Save More Lives with Therapy Assurance.
VF Therapy Assurance is the only technology to provide an additional safety net for difficult-to-detect ventricular arrhythmias. Without VF Therapy Assurance, ventricular tachyarrhythmias with low and varying signal amplitudes may not be successfully identified.13, 14
of patients who received HV therapy due to VF Therapy Assurance's enhanced detection would have been otherwise untreated for potentially life-threatening arrhythmias.13
Why Do We Implant Defibrillators?
Because every patient deserves life-saving therapy.
Abbott's ICD and CRT-D platforms are designed with patient outcomes in mind. Rob, a Navy veteran, experienced a cardiac arrest that required five shocks on the way to the hospital. With a Gallant™ ICD implant, Rob and his family now feel confident he's receiving the life-saving therapy he needs.
MR Conditional with LBB Lead*
MR Conditional with UltiPace™ Pacing Lead in the left bundle branch (LBB) area when used in the LV IS-1 port.*
With Abbott-exclusive No Wait 1.5T and 3T MRI, ensure your patients can get the scans they need, when they need it.‡
Abbott's MRI-ready solutions ensure no loss of CRT therapy for your patients in full-body scans and allows for MRI Timeout programming.**
Stay Informed
Sign up to hear about our technology, education opportunities, and more.
Read the Latest Blog Article
Stay up to date with recent news, product highlights, and case studies.
References
- Improved ICD Shock Efficacy using Programmable Pulse Width. Michael Katcher, MD; Kevin Davis, BS; Nima Badie, PhD; Luke C. McSpadden, PhD; Ulrika Birgersdotter-Green, MD; Jacqueline Joza, MD; Robert Schaller, MD; Gabriel Mouchawar, PhD. Heart Rhythm Society Conference. April 24-27, 2025
- Swerdlow C., Brewer J., Kass R., Kroll M. (1997). Application of models of defibrillation to human data: Implications for optimizing implantable defibrillator capacitance. Circulation 96(9),pgs. 2813-2822.. DOI: 10.1161/01.CIR.96.9.2813
- Ellenbogen K., Wilkoff, G., Kay G., Lau C. (2007). Clinical Cardiac Pacing, Defibrillation, and Resynchronization Therapy (3rd ed.). Elsevier Saunders; pg 542-547. ISBN-13: 978-1- 4160-2536-8
- Kawata, U., Birgersdotter- Green, U. (2018). Ventricular Fibrillation and Defibrillation, Encyclopedia of Cardiovascular Research and Medicine. Elsevier, pgs 674- 682. ISBN 9780128051542. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12- 809657-4.99764-3
- Efimov, I., Kroll, M., Tchou, P. (2009). Cardiac Bioelectric Therapy. Springer, pgs. 468- 472. ISBN 978-0-387-79403- 7
- Kroll, M., Lehmann, M. (1996). Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Therapy. Kluwher Academic Publishers, pgs. 68 -69.
- Gold, M., Shorofsky S. (1997). Strength-duration relationship for human transvenous defibrillation. Circulation 96:3517-3520.
- Kroll, M., Swerdlow, C. (2007). Optimizing defibrillation waveforms for ICDs. Journal of Interv Card Electrophysiol 18:247-263. DOI 10.1007/s10840-007- 9095-z
- Doshi, S., Pittaro, M., Reeves, M., Boyce, K., Payne, J., Kroll, M., Graumann, R., Oza, A., Val- Mejias, J. (2012). Efficacy of Tuned Waveforms Based on Different Membrane Time Constants on Defibrillation Thresholds: Primary Results from the POWER Trial. PACE Vol. 00. Pg. 8. DOI: 10.1111/j.1540- 8159.2012.03500.
- Thibault B, Waddingham P, Badie N, Mangual JO, McSpadden LC, Betts TR, Calò L, Grieco D, Leyva F, Chow A. Acute Electrical Synchronization Achieved With Dynamic Atrioventricular Delays During Biventricular and Left Ventricular MultiPoint Pacing. CJC Open. 2024 Nov 8;7(2):166-175. doi: 10.1016/j.cjco.2024.11.003
- Varma, N., Gain in CRT Efficacy with Dynamic Electrical Optimization: Real World Effect of SyncAV™ CRT on Heart Failure Hospitalizations. Poster presented at EHRA. May 2020. https://www.escardio.org/Sub-specialty-communities/European-Heart-Rhythm-Association-%28EHRA%29/Research-and-Publications/EHRA-Essentials-4-You#lbt. Accessed May 15, 2020
- Varma N, Hu Y, Connolly AT, et al. Gain in real-world cardiac resynchronization therapy efficacy with SyncAV dynamic optimization: Heart failure hospitalizations and costs. Heart Rhythm. 2021;18(9):1577-1585. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2021.05.006
- Wilkoff BL, Sterns LD, Katcher MS, et al. Novel ventricular tachyarrhythmia detection enhancement detects undertreated life-threatening arrhythmias. Heart Rhythm O2. 2022;3(1):70-78. doi:10.1016/j.hroo.2021.11.009
- Stroobandt RX, Duytschaever MF, Strisciuglio T, et al. Failure to detect life-threatening arrhythmias in ICDs using single-chamber detection criteria. Pacing and clinical electrophysiology : PACE. 2019;42(6):583-594. doi:10.1111/pace.13610
- Thibault B, Waddingham P, Badie N, Mangual JO, McSpadden LC, Betts TR, Calò L, Grieco D, Leyva F, Chow A. Acute Electrical Synchronization Achieved With Dynamic Atrioventricular Delays During Biventricular and Left Ventricular MultiPoint Pacing. CJC Open. 2024 Nov 8;7(2):166-175. doi: 10.1016/j.cjco.2024.11.003
- Leonardo C, Ermenegildo R, Christof K, Amir J, Pedro M, Pascal D, Christelle M, Olivier P, Andrea G, Kwangdeok L, Wenjiao L, Haran B, Johannes S, Bernard T, Christopher R, Christophe L. Multipoint pacing is associated with improved prognosis and cardiac resynchronization therapy response: MORE-CRT MPP randomized study secondary analyses. Europace. 2024 Nov 1;26(11):euae259. doi: 10.1093/europace/euae259. Erratum in: Europace. 2025 Feb 5;27(2):euaf022. doi: 10.1093/europace/euaf022.
- Device IFUs: Abbott Tachycardia Devices Help Manual (ARTEN600307504A), Medtronic manuals (Evera XT, Amplia, Cobalt XT, and Crome), Boston Scientific manuals (NG4 Tachy ICD, NG4 Tachy CRT-D), and Biotronik (Rivacor ICDs and CRT-Ds, Acticor ICDs and CRT-Ds).
Gallant™/Entrant™ ICDs and CRT-Ds
Rx Only
Brief Summary: Prior to using these devices, please review the Instructions for Use for a complete listing of indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions, potential adverse events and directions for use.
Intended Use: The Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Defibrillator (CRT-D) devices are primarily intended for use with compatible leads detect and treat life threatening ventricular arrhythmias by providing ventricular antitachycardia pacing and ventricular cardioversion/defibrillation. In addition, these devices can detect and treat: chronic symptomatic bradyarrhythmia by providing sensing and pacing in the right ventricle; various atrioventricular conduction abnormalities by providing sensing and pacing in the right ventricle and/or right atrium. CRT-D devices sense cardiac activity and provide pacing to resynchronize the right and left ventricles.
The myMerlinPulse™ mobile application is intended for use by people who have an Abbott Medical implanted heart device and access to a mobile device. The app provides remote monitoring capability of the implanted heart device by transmitting information from the patient’s implanted heart device to the patient’s healthcare provider.
Indications: The ICD devices are indicated in patients who have already survived a cardiac arrest or are at a high risk of Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) due to VT (ventricular tachycardia) or VF (ventricular fibrillation). Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) devices are indicated for reduction of symptoms in patients who have congestive heart failure, a reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and a prolonged QRS duration. CRT-D devices are indicated in patients who meet the CRT indications and have already survived a cardiac arrest or are at a high risk of Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) due to VT (ventricular tachycardia) or VF (ventricular fibrillation). The device is most commonly implanted within a device pocket in the pectoral region.
The myMerlinPulse™ mobile application is indicated for use by patients with supported Abbott Medical implanted heart devices.
Contraindications: Contraindications for use of the pulse generator system include ventricular tachyarrhythmias resulting from transient or correctable factors such as drug toxicity, electrolyte imbalance, or acute myocardial infarction.
The myMerlinPulse™ mobile application is contraindicated for use with any implanted medical device other than supported Abbott Medical implanted heart devices.
Adverse Events: Possible adverse events associated with the implantation of the pulse generator system include the following: Arrhythmia (for example, accelerated or induced), Bradycardia, Cardiac or venous perforation, Cardiac tamponade, Cardiogenic shock, Death, Discomfort, Embolism, Endocarditis, Erosion, Exacerbation of heart failure, Excessive fibrotic tissue growth, Extracardiac stimulation (phrenic nerve, diaphragm, pectoral muscle), Extrusion, Fluid accumulation within the device pocket, Formation of hematomas, cysts, or seromas, Heart block, Hemorrhage, Hemothorax, Hypersensitivity, including local tissue reaction or allergic reaction, Infection, Keloid formation, Myocardial damage, Nerve damage, Occlusion/Thrombus, Pericardial effusion, Pericarditis, Pneumothorax, Pulmonary edema, Syncope, Thrombosis, Valve damage. Complications reported with direct subclavian venipuncture include pneumothorax, hemothorax, laceration of the subclavian artery, arteriovenous fistula, neural damage, thoracic duct injury, cannulation of other vessels, massive hemorrhage and rarely, death. Among the psychological effects of device implantation are imagined pulsing, depression, dependency, fear of premature battery depletion, device malfunction, inappropriate pulsing, shocking while conscious, or losing pulse capability. Possible adverse device effects include complications due to the following: Abnormal battery depletion, Conductor fracture, Device-programmer communication failure, Elevated or rise in defibrillation/cardioversion threshold, Inability to defibrillate or pace, Inability to interrogate or program due to programmer or device malfunction, Incomplete lead connection with pulse generator, Inhibited therapy including defibrillation and pacing, Inappropriate therapy (for example, shocks and antitachycardia pacing [ATP] where applicable, pacing), Interruption of function due to electrical or magnetic interference, Intolerance to high rate pacing (for example dyspnea or discomfort), Lead abrasion, Lead fracture, Lead insulation damage, Lead migration or lead dislodgement, Loss of device functionality due to component failure, Pulse generator migration, Rise in DFT threshold, Rise in pacing threshold and exit block, Shunting of energy from defibrillation paddles, System failure due to ionizing radiation. Additionally, potential adverse events associated with the implantation of a coronary venous lead system include the following: Allergic reaction to contrast media, Breakage or failure of implant instruments, Prolonged exposure to fluoroscopic radiation, Renal failure from contrast media used to visualize coronary veins.
No potential adverse events have been identified with use of the myMerlinPulse™ mobile application.
‡ No minimum length of time requirement between implant and MRI scan. Stability of pacing capture thresholds is required prior to MRI scan
* MR conditional with our UltiPace™ Pacing Lead in the left bundle branch area (LBBA) using LV IS-1 port with Gallant™ and Entrant™ CRT-D models. For additional information about specific MR Conditional ICDs, leads, including scan parameters, warnings, precautions, adverse conditions to MRI scanning, and potential adverse events, please refer to Abbott MRI-Ready Systems Manual at manuals.eifu.abbott.
** No Loss of CRT therapy only applicable for select Gallant models.
MAT-2111546 v10.0


.png)
.png)
