About
Quartet Quadripolar LV Lead
More pacing flexibility without compromising lead stability.
Built on the proven QuickFlex™ µ lead platform, the Quartet™ Quadripolar LV Lead offers superb deliverability with exceptional stability and performance. Studies reflect an implant success rate averaging approximately 97%.1,2
Better Management of Heart Failure (HF) Symptoms
We designed our groundbreaking quadripolar technology to enable improved management and outcomes for HF patients. With four electrodes and up to 14 pacing configurations, the quadripolar system enables left ventricular (LV) pacing at the preferred site without compromising lead stability, for better management of heart failure patients.3
HF patients who undergo implantation of unipolar and bipolar CRT devices may experience challenges such as phrenic nerve stimulation, high pacing thresholds and non-response to CRT therapy.4 Managing these challenges can result in longer implant times and surgical revisions.
Quadripolar technology can help you overcome these challenges by offering you more pacing flexibility without compromising lead stability.
Potential Benefits of Quadripolar Technology
- Shorter implant times and decreased fluoroscopic exposure1,5
- Fewer surgical revisions2
- More basal pacing opportunities (pacing basally has been shown to be associated with improved outcomes)6,7
Overall, quadripolar technology can lead to greater CRT implant and postoperative efficiencies while providing improved CRT efficacy.
MRI Readiness
The Quartet Quadripolar LV Lead, when combined with approved devices, allows full-body, 1.5T and 3T MRI scans that meet certain scan conditions.*
- Meets industry-standard MRI testing requirements
- Capable of full body 1.5T and 3T MRI imaging scans
Multiple Shape and Spacing Options
- Distal shape options include the Double Bend shape, Traditional S-shape, Traditional S-shape—wide spacing and Small S-shape.
- Total electrode spacing options include 40, 47 and 60 mm.
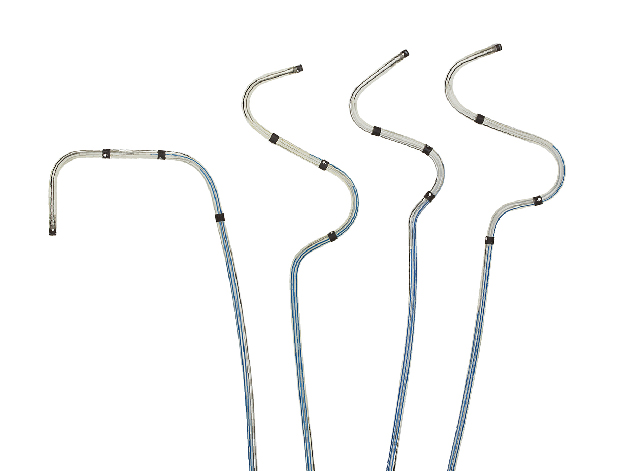

Four Distinctly Spaced Electrodes
- Enables greater pacing flexibility than unipolar or bipolar leads
- Provides more options to help prevent pacing complications
IS4 Connector
- Enables four pacing electrodes in a single connector for streamlined implantation
Low Profile
- 4.7 F lead body diameter for maneuverability
- 4.0 F tip electrode, which aids access to small targets or difficult-to-reach branch veins
Steerable Tip
- Adjustable distal tip angle for enhanced maneuverability in venous anatomy
Optim™ Lead Insulation
- First-of-its-kind hybrid insulation material
- Developed specifically for cardiac lead use
- Blends the biostability and flexibility of high-performance silicone rubber with the strength, tear resistance and abrasion resistance of polyurethane, allowing for superior abrasion resistance in a thin diameter lead8
*See MRI Ready Systems Manual for device and lead combinations and associated MRI scan parameters. Quartet quadripolar LV Lead is MR Conditional in the 86cm lead length.
References
- Sperzel, J., Dänschel, W., Gutleben, K. J., Kranig, W., Mortensen, P., Connelly, D., … Rinaldi, C. A. (2012). First prospective, multi-centre clinical experience with a novel left ventricular quadripolar lead. Europace, 14(3), 365-372
- Forleo, G. B., Della Rocca, D. G., Papavasileiou, L. P., Molfetta, A. D., Santini, L., & Romeo, F. (2011). Left ventricular pacing with a new quadripolar transvenous lead for CRT: Early results of a prospective comparison with conventional implant outcomes. Heart Rhythm, 8(1), 31-37. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2010.09.076
- Data compiled from clinical study results, on file in Report 60034670.
- Thibault, B., Dubuc, M., Guerra, P. G., Karst, E., Ryu, K., Paiement, P., … Farazi, T. (2011). Electrode selection to avoid phrenic stimulation with a quadripolar left heart lead. Heart Rhythm, 8(5), S68. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2011.03.023
- Duray, G. Z., Hohnloser, S. H., & Israel, C. W. (2008). Coronary sinus side branches for cardiac resynchronization therapy: Prospective evaluation of availability, implant success, and procedural determinants. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 19(5), 489-494. https://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8167.2007.01096.x
- Singh, J. P., Klein, H. U., Huang, D. T., Reek, S., Kuniaa, M. Quesada, A., … Moss, A. J. (2011). Left ventricular lead position and clinical outcome in the Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (MADIT-CRT) trial. Circulation, 123(11), 1159-1166. https://dx.doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.000646
- Merchant, F. M., Heist, E. K., McCarty, D., Kumar, P., Das, S., Blendea, D., … Singh, J. P. (2010). Impact of segmental left ventricle lead position on cardiac resynchronization therapy outcomes. Heart Rhythm, 7(5), 639-644. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2010.01.035
- Jenney, C., Tan, J., Karicherla, A., Burke, J., & Helland, J. (2005). A new insulation material for cardiac leads with potential for improved performance. Heart Rhythm, 2(5), S318-319. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2005.02.1004
MAT-2512199 v1.0
