Advancements in pacemaker technology have introduced smaller devices, more physiologic shapes, MR Conditional systems, remote monitoring, and increased device longevity. Abbott offers multiple pacemaker options with unique functionality so you and your team can determine the best solution for your patients’ conditions.
AVEIR™ AR Atrial Leadless Pacemaker
The AVEIR AR Leadless Pacemaker is the only single chamber atrial leadless pacemaker that offers a safe1, effective1, and upgradeable2 pacing solution for patients with sinus node dysfunction and normal AV and intraventricular conduction systems.3
AVEIR™ VR Ventricular Leadless Pacemaker
The AVEIR VR leadless pacemaker is the next evolution in leadless technology that has been designed for long-term retrieval4, an extended battery life5,6, mapping prior to fixation for optimal device location5,7, and provides an upgradeable platform to later support dual chamber pacing when the patient therapy need evolves.
AVEIR™ DR Dual Chamber Leadless Pacemaker System
The AVEIR DR Dual Chamber Leadless Pacemaker System is a first-of-its kind, dual chamber leadless pacing system featuring both atrial and ventricular pacing and sensing, beat-to-beat synchrony, an upgradeable system,2 long term retrieval,4 and mapping prior to fixation.1,3
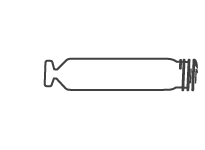
Assurity MRI™ Pacemaker
The Assurity MRI pacemaker is the world’s smallest, longest-lasting wireless MRI pacemaker.8*** The greater longevity of the Assurity MRI pacemaker reduces the chance of potential device replacement, which means less risk for infection and complications.9 No wait 3T and 1.5T MRI options ensure your patients can get the care they need when they need it.
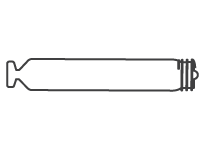
Endurity™ Pacemaker
Designed for ease of implant and a smaller incision and pocket size, the Endurity pacemaker can help reduce RV pacing and heart-failure hospitalization with beat-by-beat ventricular support.10
References
* Limited data is available for Aveir LP. The Aveir LP’s predicate device has chronic retrieval success rate >80% with helix fixation through 7 years regardless of implant duration
** ISO standard settings: VVIR, 60bpm, 2.5V @0.4 ms, 600 Ω, 100% pacing
***Among pacemakers < 15cc in total volume; as of February 1, 2017.
- Knops, Reinoud E., et al. "A Dual-Chamber Leadless Pacemaker." New England Journal of Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2300080
- AVEIR™ Leadless Pacemakers and Delivery Catheter IFU, ARTEN600307044.
- AVEIR DR CE Mark and FDA approval.
- Reddy VY, et al. Worldwide Experience with Leadless Pacemaker Retrievals: A Worldwide Nanostim Experience out of 9y. Presented at: APHRS 2022; Nov 18-20, 2022; Singapore.
- Aveir™ VR Leadless Pacemaker and Delivery Catheter IFU. ARTEN600175957.
- Micra‡ VR IFU M991010A001 REV. B
- Reddy, VY et al. Primary Results on Safety and Efficacy from the LEADLESS II-Phase 2 Worldwide Clinical Trial, JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology, 2021, ISSN 2405-500X, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacep.2021.11.002.
- St. Jude Medical. St. Jude Medical Research Report: Competitive Product Review: Wireless Pacemakers. No. 60082151. Rev B.
- Romeyer-Bouchard, C., Da Costa, A., Dauphinot, V., Messier, M., Bisch, L., Samuel, B, ... Isaaz, K. (2010). Prevalence and risk factors related to infections of cardiac resynchronization therapy devices. European Heart Journal, 31(2), 203-210. https://dx.doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehp421
- Faulknier, B., & Richards, M. (2012, December). The association of the use of the ventricular intrinsic preference (VIP™) feature with heart failure hospitalization in pacemaker patients. Presented at the XV International Symposium on Progress in Clinical Pacing, Rome, Italy.
™ Indicates a trademark of the Abbott group of companies.
‡ Indicates a third-party trademark, which is property of its respective owner.
MAT-2010034 v3.0 | OUS