Unparalleled Safety with XIENCE™ Stent1
XIENCE™ Stent's Excellent Outcomes in Complex Patients2-4
Early outcomes with XIENCE™ Stent, implanted in complex patients, reveal excellent rates of definite stent thrombosis (ST) at 30 days:
- Bifurcations Lesions: 0.0%2
- Calcified Lesions: 0.0%3
- Long Lesions: 0.3% ST4

Lower Early Stent Thrombosis Rates with XIENCE™ Stent vs Other DES
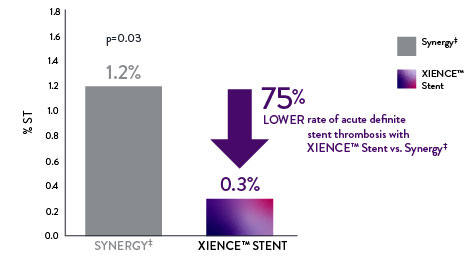
XIENCE™ Stent Acute ST Rate 75% Lower vs Other DES
With XIENCE™ Stent there is a 75% lower rate of acute (24-hour) definite ST compared to Synergy‡.5
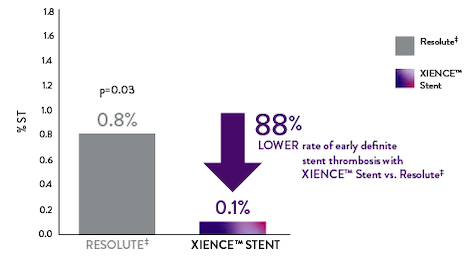
XIENCE™ Stent Early ST Rate 88% Lower vs Other DES
With XIENCE™ Stent there is an 88% lower rate of early (30-day) definite ST compared to Resolute‡.6
Consistently Lowest Rates of Late and Very Late Stent Thrombosis
XIENCE™ Stent has the most exceptional rates—and consistently the lowest rates—of late and very late ST.1 It’s another example of how XIENCE™ Stent delivers unparalleled patient outcomes which last far beyond the intervention.1
Even when examining ultra-long-term safety, XIENCE™ Stent reveals excellent patient outcomes—0.8% ST 10 years after PCI.12

References
- Zanchin C, et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12(17):1665-1675. Serruys P, et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:136-146. Shiomi H, et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:637-647. Kufner S, et al. Circulation. 2019:139(3):325-333. Palmerini T, et al. Lancet. 2013;379:1393-1402. Bangalore S, et al. Circulation. 2012;125:2873-2891. Bangalore S, et al. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;6(6):378-390. Pilgrim T, et al. Lancet. 2014;384:2111-2122. Pilgrim T, et al. Lancet. 2018;392:737-746. Data on file at Abbott.
- Džavík V, et al. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;82(3):E163-E172.
- Onuma Y, et al. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2010;76:634-642.
- Hong S, et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;9:1438-1446.
- Zanchin C, et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12(17):1665-1675.
- Serruys P, et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:136-146.
- von Birgelen C, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59:1350-1361.
- Natsuaki M, et al. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2016 31(3):196-209.
- van Geuns RJ, et al. TCT 2019. IDEAL-LM.
- Chevalier B, et al. EuroIntervention. 2018;13:1561-1564.
- Gao R, et al. TCT 2019. ABSORB China.
- Kufner S, et al. Circulation. 2019:139(3):325-333.
MAT-2413628 V1.0

