XIENCE™ Stent in AMI Patients
Low long-term event rates are critical for acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients, and XIENCE™ Stent findings show excellent early outcomes in AMI patients.2 Contributing to these results are several features of XIENCE™ Stent:
- Innovative stent design
- Anti-thrombotic fluoropolymer3
- Market-leading everolimus4
XIENCE™ Stent AMI Safety Data Apparent at 2 Weeks
The XIENCE™ Stent fluoropolymer exhibits improved anti-inflammatory characteristics compared to other drug-eluting stents (DES).3 This may be a key factor why the XIENCE™ Stent has such impressive safety data within 2 weeks post percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) among AMI patients. Data show that—compared to immediately post intervention—XIENCE™ Stent reveals significant progression at 2 weeks post PCI2 in terms of:
- Better strut coverage (p<0.01)
- Less thrombus (p=0.03)
- Larger average lumen area (p=0.048)
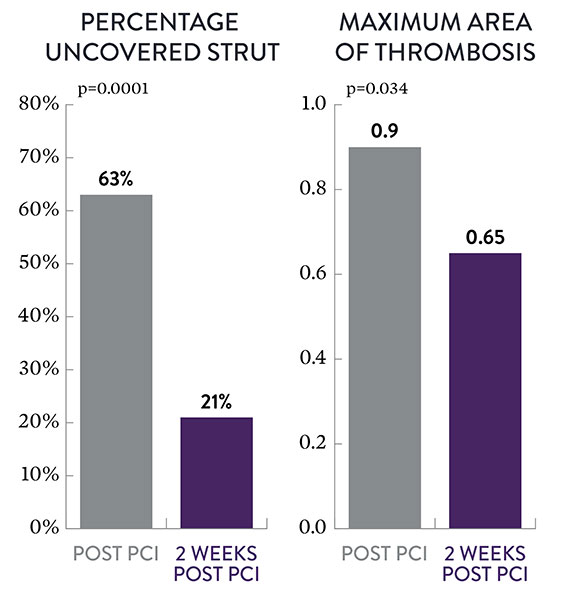
Strut Coverage and Thrombosis2

Post PCI

2 Weeks Post PCI
Less Thrombosis, Larger Lumen Area at 2 Weeks2
XIENCE™ Stent 4-Year AMI Study5
A large, multicentre, real-world study revealed that the XIENCE™ Stent low clinical event rates at 1 year were sustained through 4 years—in both AMI and non-AMI patients.
At 1 Year and 4 Years No Significant Difference in AMI and Non-AMI Patients


EXAMINATION STEMI Data: Low XIENCE™ Stent Acute ST6
XIENCE™ Stent also demonstrates safety among ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients, a subgroup of AMI patients. At 30 days, the rate of definite stent thrombosis (ST) with XIENCE™ Stent vs bare metal stents (BMS) was significantly lower: 0.4% vs 1.6%, p=0.02.
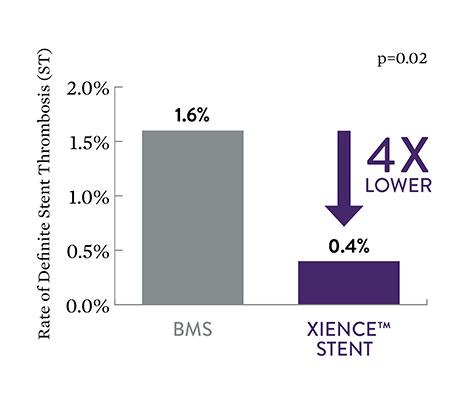
XIENCE™ Stent STEMI Data at 1 Year6
At 12 months 98% of patients with STEMI are free of target lesion revascularisation (TLR).

XIENCE™ Stent Long-Term STEMI Data7
The EXAMINATION trial looked at the AMI subgroup of STEMI patients, a subgroup of AMI patients. At both 1 and 5 years XIENCE™ Stents performed better than BMS in an all-comer population.6,7
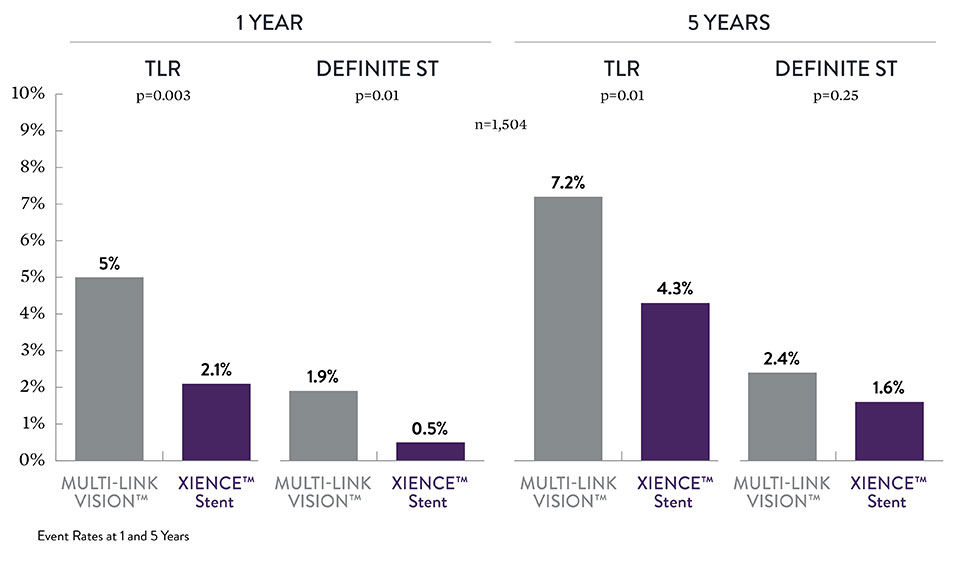
Event Rates at 1 and 5 Years
“The benefit of EES in ST-elevation myocardial infarction at long term is reassuring and confirms the use of [XIENCE™] second-generation stents as the current gold standard treatment in this clinical context.”
—Manel Sabaté, et al.7
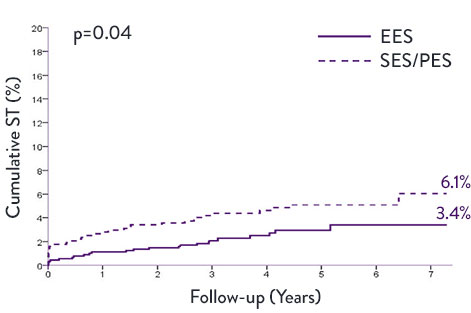
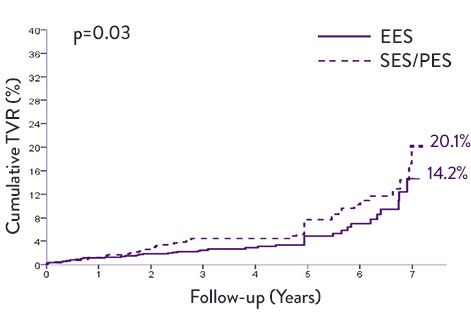
XIENCE™ Stent Very Long-Term STEMI Data—7 Years8
A meta-analysis examined trials (n=1,581) comparing XIENCE™ Stent second generation DES vs first generation DES—sirolimus-eluting stents (SES) and paclitaxel-eluting stents (PES). XIENCE™ Stent conferred significantly lower rates of ST and target vessel revascularisation (TVR) at 7 years.
XIENCE™ vs First-Generation DES in STEMI Patients
Very Low 1-Year Event Rates in STEMI Registry9
One-year clinical outcomes from the XIENCE™ Stent STEMI Registry further revealed that the XIENCE™ Stent was associated with a low incidence of clinical events—including stent thrombosis—even in a high-risk STEMI population.



References
- Zanchin C, et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12(17):1665-1675. Serruys P, et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:136-146. Shiomi H, et al. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:637-647. Kufner S, et al. Circulation. 2019:139(3):325-333. Palmerini T, et al. Lancet. 2013;379:1393-1402. Bangalore S, et al. Circulation. 2012;125:2873-2891. Bangalore S, et al. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;6(6):378-390. Pilgrim T, et al. Lancet. 2014;384:2111-2122. Pilgrim T, et al. Lancet. 2018;392:737-746. Data on file at Abbott.
- Morino Y, et al. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2019;34:14-24.
- Jinnouchi H, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:Suppl B – TCT-291.
- Data on file at Abbott.
- Sudhir K, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64(11 Suppl) – TCT-39.
- Sabaté M, et al. Lancet. 2012;380:1482-1490.
- Sabaté M, et al. Lancet. 2016;387:357-366.
- De Luca G, et al. Int J Cardiol. 2017;244:121-127.
- Otsuji S, et al. EuroPCR 2019 – XIENCE STEMI Registry.
MAT-2413843 V1.0

