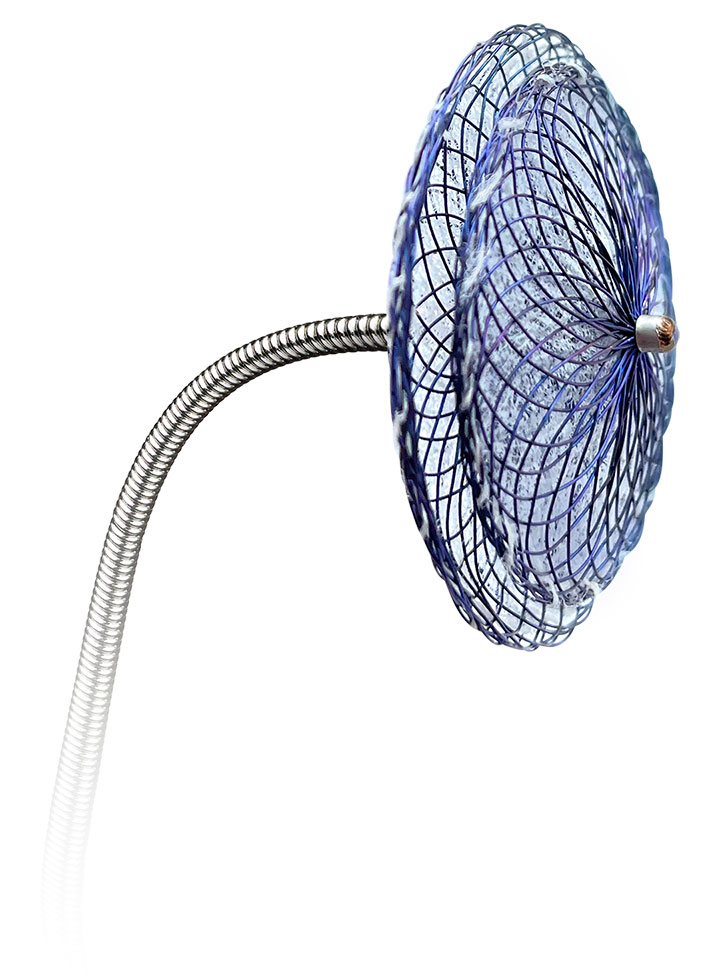
Effective PFO Closure Made Easier1
Over 25 years ago, we pioneered PFO closure with the Amplatzer™ PFO Occluder. Today, it is the most-studied — and most-trusted — device of its kind, with over 180,000 patients treated worldwide.2
And our clinical evidence is unmatched, thanks to the largest-ever trial for PFO closure, boasting 5,810 patient-years of data.3
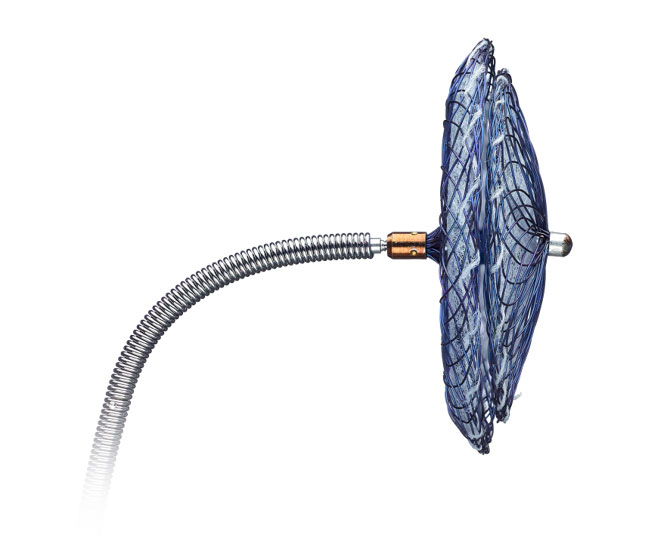
With the introduction of the Amplatzer Talisman PFO Occluder, we have built upon the proven Amplatzer PFO closure technology. The occluder now comes assembled and ready to use, simplifying prep and enhancing ease-of-use. And we've refined the 30mm size to have a smaller left atrial disc to better avoid interference with surrounding structures.
The easy-to-use just got easier.

Ordering Information
| Sizing and Device Selection | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Amplatzer™ Talisman™ PFO Occluder | |||
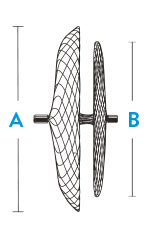
| Model/Reorder Number | Right Atrial Disc Diameter A | Left Atrial Disc Diameter B | Recommended Sheath Size |
| 9-PFO-1818 | 18 mm | 18 mm | 8 F; 45° curve |
| 9-PFO-2518 | 25 mm | 18 mm | 8 F; 45° curve |
| 9-PFO-3025 | 30 mm | 25 mm | 9 F; 45° curve |
| 9-PFO-3525 | 35 mm | 25 mm | 9 F; 45° curve |
| Delivery Sheath | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplatzer™ Talisman™ Delivery Sheath | |||||
| Model/Reorder Number | Sheath Size | Tip Angle | Sheath Inner Diameter | Sheath Outer Diameter | Usable Length |
| 9-TDS-08F45-80 | 8 F | 45° | 2.69 mm | 3.45 mm | 80 cm |
| 9-TDS-09F45-80 | 9 F | 45° | 3.00 mm | 3.81 mm | 80 cm |
| Ancillary Products | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplatzer™ Guidewire | ||||
| Model/Reorder Number | Diameter | Body | Tip Description | Usable Length |
| 9-GW-002 | 0.035 inch | Super Stiff | 1.55 mm, Modified J-tip | 260 cm |
| Device Sizing Guidelines | ||
|---|---|---|
| PFO Morphology | Example Anatomical Characteristics | Suggested Amplatzer Talisman PFO Occluder size (mm) |
| Simple PFO or PFO with a non-prominent ASA PFO where a secure device position and effective PFO closure can be achieved when using the 25 mm device size |
| 25 |
| Complex PFO PFO with one or more anatomical characteristics that may complicate the ability to achieve a secure device position and effective PFO closure when using the 25 mm device size |
| 30 or 35 |
| PFO with small anatomy Anatomy not suitable for 25 mm device size secondary to interference with adjacent cardiac structures |
| 18 |
Note: Evaluate the position of the device after deployment, but before detachment. Use echocardiography to ensure that the device does not impinge on the free atrial wall or aortic root. If the device interferes with an adjacent cardiac structure (such as free atrial wall or aortic root), recapture the device and redeploy. If device position remains unsatisfactory, recapture the device and either replace with a smaller device (18 mm or 25 mm) or refer the patient for alternative treatment. The presence of an ASA alone does not necessarily prevent successful PFO closure with a 25 mm device size. In RESPECT1, 180 patients (36%) in the device closure group had an ASA. The 25 mm device size was used in the majority of patients with an ASA (77%) to close the PFO, and at 6-months post-implant, effective closure was achieved in 95% of these patients. There were no cases of device embolization in any patient in the study 1. Saver JL, Carroll JD, Thaler DE, et al. Long-term outcomes of patent foramen ovale closure or medical therapy after stroke. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1022-32. | ||
References
- Tests performed by and data on file at Abbott.
- Abbott data on file.
- Saver JL, Carroll JD, Thaler DE, et al. Long-term outcomes of patent foramen ovale closure or medical therapy after stroke. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377: 1022-32.
MAT-2010368 v3.0 | Item approved for OUS use only.