MAT-2105201 v1.0
Unmatched 1-Year Patency & 3-Year Freedom From TLR
The Supera™ Stent has been studied in over 2,000 patients worldwide in the SUPERB trial and 16 retrospective studies. Notably, in all of the 17 studies, the Supera™ Peripheral Stent showed durable results with zero fractures at 1 year.1,4-19
superb Trial
At 1 year the Supera™ Stent demonstrated primary patency of 91% when nominally* deployed. At 3 years, freedom from targeted lesion revascularisation (tlr) was 94% when nominally* deployed.1
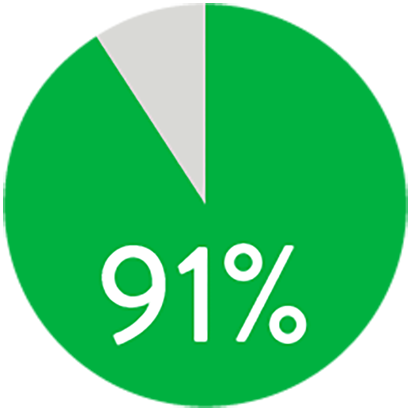
patency (k-m) at 1 year
When nominally deployed*
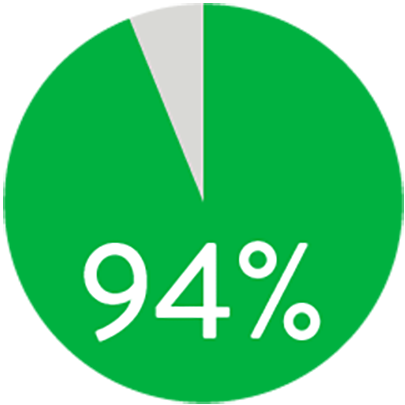
freedom from tlr at 3 years
When nominally deployed*
*Nominal deployment is defined as the stent length upon deployment being within +/- 10% of the labelled stent length. This data is from a non-powered post-hoc analysis. K-M=Kaplan Meier.
Consistent Patency Regardless of Lesion Length
With some peripheral stents, increasing lesion lengths can lead to decreasing patency rates.20 The Supera™ Stent stands apart for its consistently high patency rates in lesions spanning lengths from 5.3 cm up to 28.0 cm.†
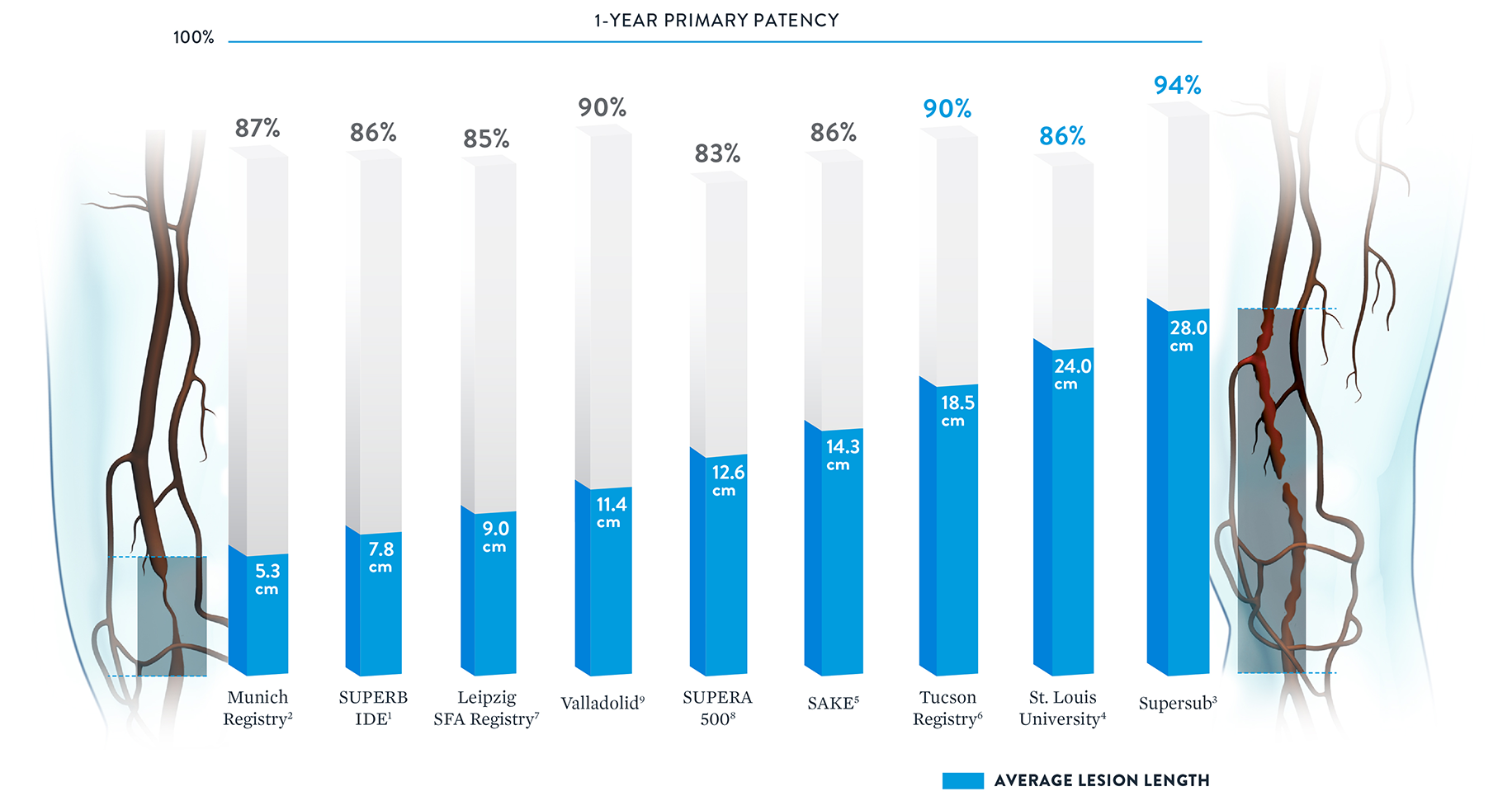
† Published data was included if lesion length and patency were both available.
Note: Results from different clinical trials are not directly comparable. Information provided for educational purposes only.
Excellent Results from Simple to Complex Lesions
Whether treating simple (tasc a&b) or complex (tasc c&d) lesions, the Supera™ Stent is associated with impressive, consistent patency performance data at 1 year.1-4
| Simple | |||
|---|---|---|---|
.png) | Trial/Study | munich registry2 | superb1 |
| Lesion Length | 5.3cm | 7.8cm | |
| TASC A&B Lesions | 100% | 94% | |
| 1-Yr Patency | 86.7% | 90.5% | |
| Sites | Single Centre | Multicentre (46 sites) | |
| # Patients | 70 | 264 | |
| Complex | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | Trial/Study | st. louis4 | supersub3 |
| Lesion Length | 24cm | 28cm | |
| TASC C&D Lesions | 78% | 100% | |
| CTOs | Unknown | 100% | |
| 1-Yr Patency | 85.6% | 94.1% | |
| Sites | Single Centre | Single Centre | |
| # Patients | 48 | 34 | |
TASC: Trans-Atlantic Inter-Society Consensus
REFERENCES
- Garcia L. et al., Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 2017 Jun 1;89(7):1259-1267.
- Treitl, K.M., et al. European Radiology.2017; 10.1007.
- Palena L.M. et al. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Intervention.2016.
- Brescia AA. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2015 Jun;61(6):1472-8
- George JC. et al., J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014 Jun;25(6):954-61.
- Montero-Baker M. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2016 Oct;64(4):1002-8.
- Scheinert D. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2011 Dec;18(6):745-52.
- Werner M. et al., EuroIntervention. 2014 Nov;10(7):861-8.
- San Norberto EM. et al., Ann Vasc Surg. 2017 May;41:186-195.
- Chan YC. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2015 Nov;62(5):1201-9.
- Dumantepe M. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2017 Jul;51(5):240-246.
- Goltz JP. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2012 Jun;19(3):450-6.
- León LR Jr. et al., J Vasc Surg. 2013 Apr;57(4):1014-22.
- Myint M. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2016 Jun;23(3):433-41.
- Palena LM. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2018 Oct;25(5):588-591.
- Scheinert D. et al., JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013 Jan;6(1):65-71.
- Steiner S. et al., J Endovasc Ther. 2016 Apr;23(2):347-55.
- Teymen B. et al., Vascular. 2018 Feb;26(1):54-61.
- Bhatt H. et al., Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2018 Jul;19(5 Pt A):512-515.
- Shroë H. Superficial femoral artery PTA or stenting? 5-Year results. CIRSE 2011; Munich, Germany
MAT-2409315 v1.0

