OCT with MLD MAX Workflow Improves PCI Decision-Making, Safety and Procedural Efficiency1
OCT with MLD MAX workflow changed physician PCI decision-making in 86% of lesions compared to angiography.1

OCT with MLD MAX workflow reduced radiation exposure by 10.7% with no difference in contrast use compared to angiography.2

Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is mostly guided by angiography which has well-established limitations:
- Inaccurate visual estimation of luminal dimensions1
- Little to no information on plaque morphology, vascular remodeling, or atherosclerosis burden1
- Inability to detect underexpansion, malapposition and edge dissection1
Multi-phase LightLab data gives further insights into the limitations of angiography in the cath lab and highlights the benefits of using intravascular imaging with OCT.
What is LightLab?
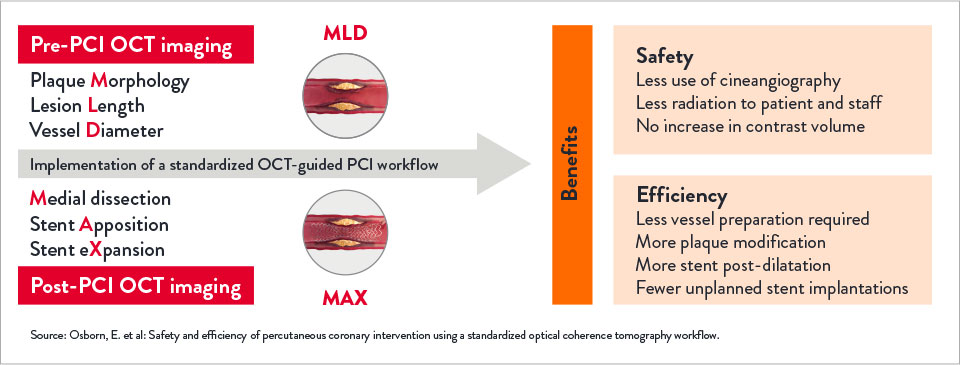
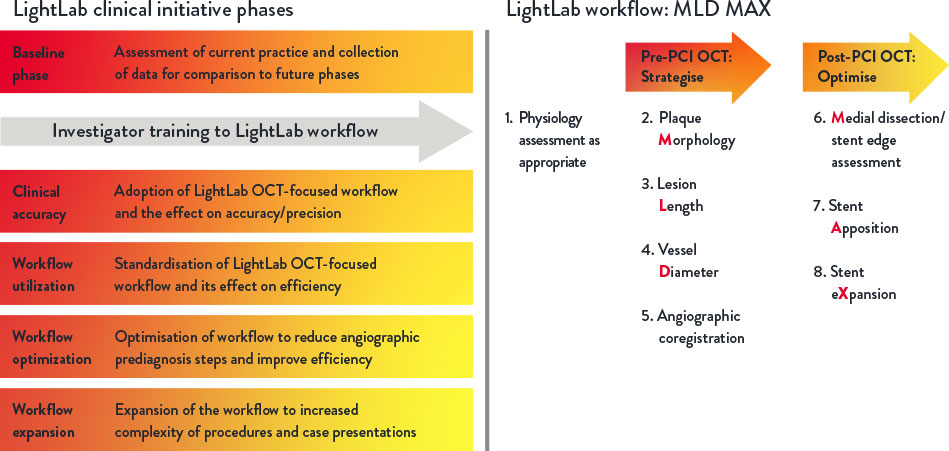
The LightLab Clinical Initiative (“LightLab”) is a multicentre, prospective, observational clinical initiative designed to evaluate the impact of using a standardised OCT workflow, MLD MAX, on physician decision-making and procedural efficiency.
The workflow facilitates utilisation of OCT information to guide treatment decisions during PCI: assessment of lesion Morphology, Length, and Diameter (MLD) from pre-PCI OCT pullback and optimisation of stent placement for Medial dissection, stent Apposition, and stent Xpansion (MAX) from the post-PCI OCT pullback.
How Does OCT with MLD MAX Impact PCI Decision-Making?
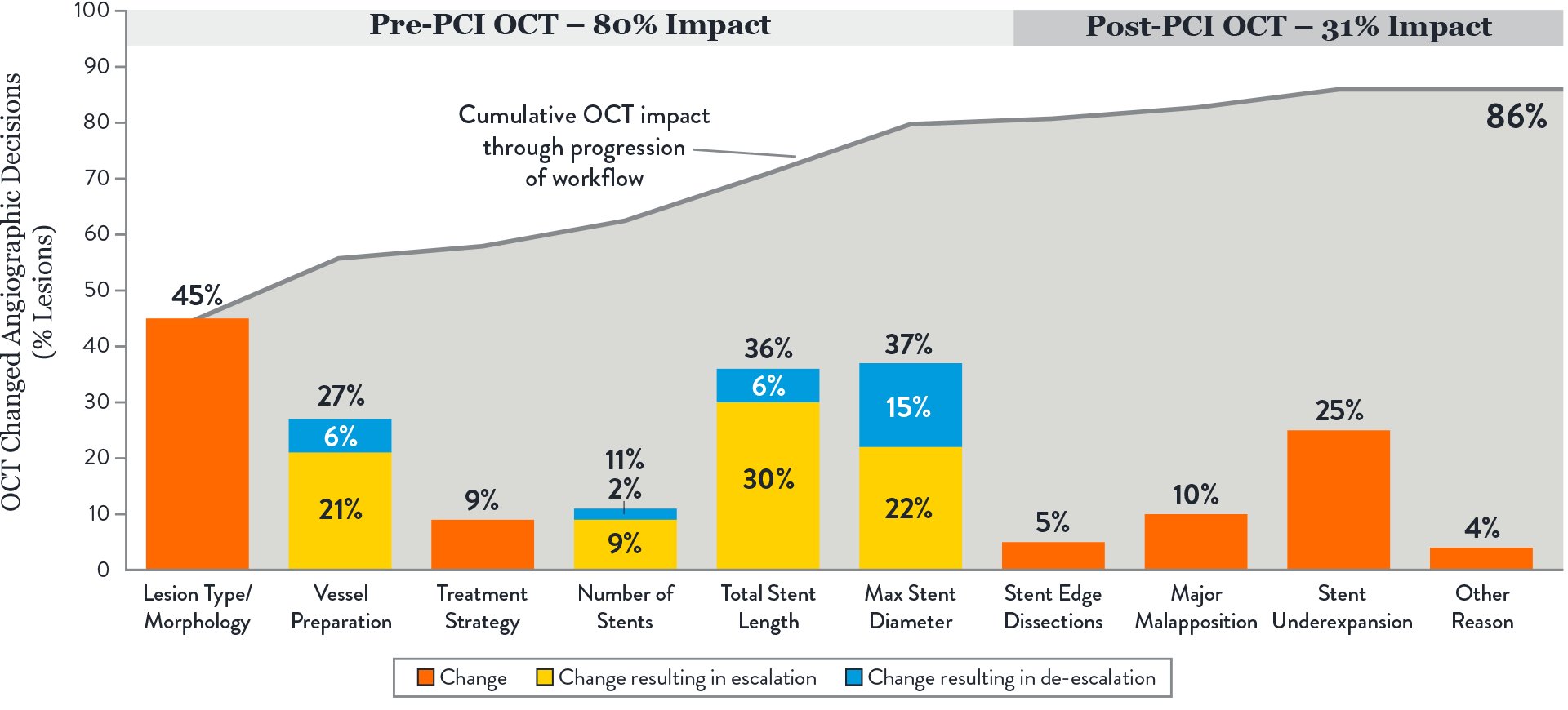
OCT with MLD MAX workflow changed physician PCI decision-making in 86% of lesions compared to angiography.1 The impact of OCT was consistent regardless of operator’s prior OCT experience.1
Key takeaways:
1. The largest impact of OCT-guided assessment over angiography was observed prior to stenting, in pre-PCI OCT or MLD steps.1
These steps involve morphology assessment (M), stent sizing (L&D) and vessel preparation, key decisions which may influence final stent expansion. Achieving optimal expansion is proven to reduce rates of major adverse cardiac events during PCI.3
2. OCT changed angio-based assessment of lesion morphology in 45% of lesions and subsequently impacted vessel prep strategy.1
OCT provides additional information on lesion morphology (plaque type composition) which informs how to prepare and treat the vessel appropriately, especially when calcification is present. Severity of calcification was underestimated in 85% of lesions when using angiography alone. Extensive calcification may adversely impact PCI procedure and final stent expansion.3
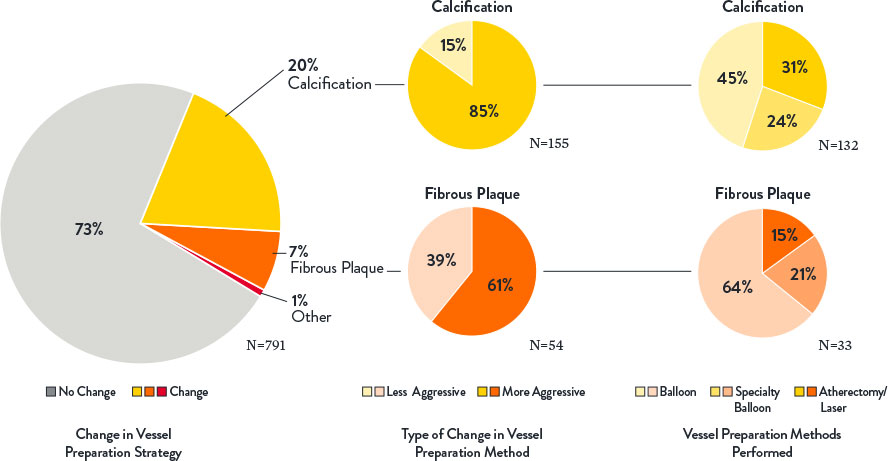
Source: Bergmark et al: Decision-Making During Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Guided by Optical Coherence Tomography: Insights From the LightLab Initiative
3. Optimal stent expansion was achieved with MLD MAX workflow.1
The use of MLD MAX workflow helped achieve 80% stent expansion on average compared to 76% average stent expansion in lesions before stent optimisation. Data from trials and registries have demonstrated that achieving a minimal stent area >4.5 mm2 and/or a stent expansion of >80% using OCT is associated with lower major adverse clinical events.4
OCT makes it easy to detect underexpansion. Ultreon™ 1.0 Software displays instantaneous calculations of expansion and apposition values, reference lumen diameter and lumen diameter values in color-coded markers: stent underexpansion indicator—orange, stent malapposition indicator—yellow.6
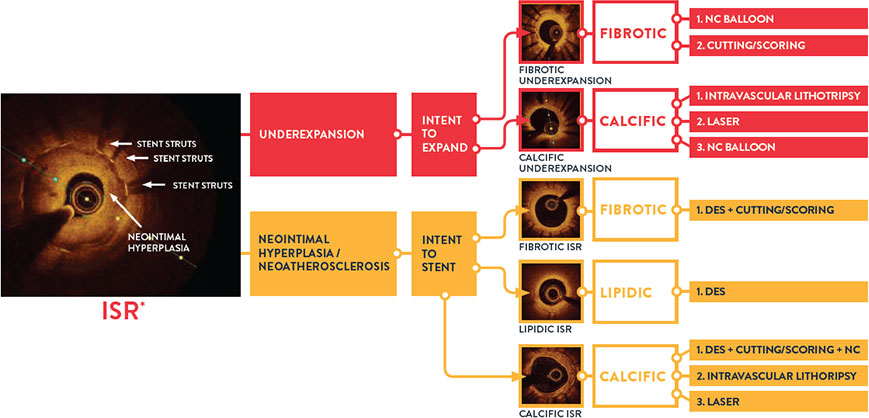
4. Pre-PCI OCT changed angio-based diagnosis and treatment decisions in ISR lesions.7
When physicians used OCT pre-PCI in ISR lesions, they changed their angiographic diagnosis and treatment strategy in 91% of lesions. OCT can identify ISR and the mechanism of stent failure which impacts ISR treatment strategy. In LightLab, OCT changed angio assessment of ISR mechanism in 48% of lesions.
Identifying the mechanism of stent failure is paramount to planning treatment because treatment strategy is different for ISR due to stent underexpansion and ISR due to neointimal hyperplasia.3 Analysis of ISR by intravascular imaging is essential to understand the mechanism of failure and OCT is a preferred technique.3
Algorithm adapted from: Ziad Ali, MD. CHIP guided by OCT, A Case Based Discussion, TCT 2017
How Does OCT With MLD MAX Impact PCI Safety and Efficiency?
OCT with MLD MAX reduced radiation exposure by 10.7% with no difference in contrast use.2
Implementing OCT with MLD MAX workflow pre- and post-PCI improves PCI safety and efficiency compared to PCI guided by angiography alone.2
Key takeaways:
- OCT with MLD MAX reduces radiation exposure by 10.7% and improves procedural safety.2
The detailed information provided by OCT diminishes reliance on angiography, resulting in fewer cineangiography runs (and no difference in contrast use) and less overall case radiation to patient and cath lab staff.2
- OCT with MLD MAX improves procedural efficiency.2
The detailed information provided by OCT decreased the need for universal vessel preparation and improved device selection based on proper plaque modification and precise stent sizing selection.2
When operators use OCT with the full MLD MAX workflow (pre-PCI OCT and post-PCI OCT) vs performing post-PCI OCT only, procedural benefits include reduced rate of underexpansion and malapposition, reduced use of contrast and decreased need for further optimisation.5
OCT imaging with MLD MAX workflow supports complete vessel evaluation, proper lesion preparation and optimisation which are critical to achieve optimal stent expansion. Inadequate stent expansion is the most important predictor of subsequent stent failure due to stent thrombosis (ST) or restenosis.2
About LightLab Study
LightLab structure and phases
LightLab is a multiphase prospective observational data-gathering study conducted between January 2019 and June 2021, with 17 participating hospitals and physicians in the US. Data were gathered in real-time, where OCT guidance was employed during PCI using a standardised OCT-guided workflow MLD MAX.
The LightLab Clinical Initiative was designed in multiple phases to facilitate regular adoption of the MLD MAX workflow during PCI to improve operator and procedural efficiency, and to expand the workflow into increasingly complex procedures.
References
- Bergmark, B. et al: Decision-Making During Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Guided by Optical Coherence Tomography: Insights From the LightLab Initiative. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2022;15:e011851. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.122.011851.
- Osborn, E. et al: Safety and efficiency of percutaneous coronary intervention using a standardised optical coherence tomography workflow. EuroIntervention 2023;18:1178-1187. DOI: 10.4244/EIJ-D-22-00512.
- Räber, L. et al. Clinical use of intracoronary imaging. Part 1: guidance and optimisation of coronary interventions. An expert consensus document of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(35):3281-3300.
- Razzouk, L. et al. Workflow for Percutaneous Coronary Intervention With Optical Coherence Tomography-Guidance: MAXing the MLD? Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions. Retrieved from: http://ahajournals.org on November 16, 2022.
- Khuddus, M. et al. Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory Efficiency and Quality Improvement during Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Utilizing a Standardised Optimal Coherence Tomography (OCT) Workflow in a Real-World Setting: Results from the LightLab Initiative. CRTOnline 2021.
- Ultreon™ 1.0 Software Instructions For Use (IFU). Refer to Instructions IFU for additional information.
- Croce, K., et al: Effect of a Prescriptive Optical Coherence Tomography Guided Strategy on Treatment of In-Stent Restenosis – Insights from the LightLab Initiative. TCTConnect2020 Presentation.
MAT-2413979 V1.0