Exact placement, strength and performance where it counts.

Data on file at Abbott.
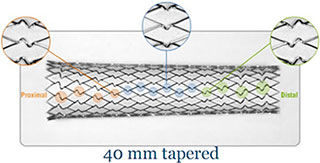
| XACT™ Carotid Stent System (FDA Part Numbers) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stent Diameter (mm) | Stock Number | ICA Reference Vessel Diameter | CCA Reference Vessel Diameter (mm) | Minimum Sheath / Guide Size | ||
| 20 (mm) | 30 (mm) | 40 (mm) | ||||
| 7.0 | 82095-01 | 82094-01 | N/A | 5.5-6.4 | N/A | 6F / 8F |
| 8.0 | 82093-01 | 82092-01 | N/A | 6.4-7.3 | N/A | 6F / 8F |
| 9.0 | 82089-01 | 82088-01 | N/A | 7.3-8.2 | N/A | 6F / 8F |
| 10.0 | 82099-01 | 82098-01 | N/A | 8.2-9.1 | N/A | 6F / 8F |
| 6.0-8.0 taper | N/A | 82091-01 | 82090-01 | 4.8-5.5 | 6.4-7.3 | 6F / 8F |
| 7.0-9.0 taper | N/A | 82087-01 | 82086-01 | 5.5-6.4 | 7.3-8.2 | 6F / 8F |
| 8.0-10.0 taper | N/A | 82097-01 | 82096-01 | 6.4-7.3 | 8.2-9.1 | 6F / 8F |
Data on file at Abbott.
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) released the final decision memo on NCD 20.7 on October 11, 2023. This expands coverage for Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS) procedure to patients for the treatment of carotid artery stenosis.
More information is available at Abbott Medicare and Medicaid Resources.
MAT-2106474 v4.0
The XACT™ Carotid Stent System (XACT™), used in conjunction with the Emboshield™ family of Embolic Protection System is indicated for the improvement of the lumen diameter of carotid arteries in patients considered at high risk for adverse events from carotid endarterectomy who require percutaneous carotid angioplasty and stenting for occlusive artery disease and meet the criteria outlined below:
Patients with carotid artery stenosis (≥ 50% for symptomatic patients by ultrasound or angiography or ≥ 80% for asymptomatic patients by ultrasound or angiography), located between the origin of the common carotid artery and the intra-cranial segment of the internal carotid artery AND
Patients must have a reference vessel diameter ranging between 4.8 mm and 9.1 mm at the target lesion.
Contraindications associated with angioplasty must be considered when using the XACT™ Carotid Stent System. These include, but are not limited to:
Only physicians who have received appropriate training and are familiar with the principles, clinical applications, complications, side effects and hazards commonly associated with carotid interventional procedures should use this device.
Refer to instructions supplied with all interventional devices to be used with the XACT™ Carotid Stent System for their intended uses, contraindications, and potential complications.
The safety and efficacy of the XACT™ Carotid Stent System has not been demonstrated with embolic protection systems other than the Emboshield™ Embolic Protection System.
The long-term performance (> 1 year) of the XACT™ Carotid Stent System has not been established.
As with any type of vascular implant, infection secondary to contamination of the stent may lead to thrombosis, pseudoaneurysm, or rupture.
Stenting across a major bifurcation may hinder or prevent future diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
In patients requiring the use of antacids and / or H2-antagonists before or immediately after stent placement, oral absorption of antiplatelet agents (e.g. aspirin) may be adversely affected.
The appropriate antiplatelet and anticoagulation therapy should be administered pre- and post-procedure as suggested in these instructions. Special consideration should be given to those patients with recently active gastritis or peptic ulcer disease.
When multiple stents are required, stent materials should be of similar composition.
The safety and effectiveness of the XACT™ Carotid Stent System has NOT yet been established in patients with the characteristics noted below.
The safety and effectiveness of concurrent treatment of lesions in patients with bilateral carotid artery disease have not been established.
PRECAUTIONS
Carefully inspect device components prior to use to verify that they have not been damaged and that the size, shape and condition are suitable for the procedure for which they are to be used. A device or access device which is kinked or damaged in any way should not be used. If pouch is damaged do not use.
Confirm the compatibility of the XACT™ Stent Delivery System with the interventional devices before actual use.
Precautions to prevent or reduce clotting should be taken when any interventional device is used. Flush or rinse all devices entering the vascular system with sterile isotonic heparinized saline prior to use.
Do not remove the stent from its delivery system as removal may damage the stent. The stent and delivery system are intended to be used in tandem. If removed, the stent cannot be put back on the delivery system.
The delivery system should not be used in conjunction with other stents.
To reduce the potential for the liberation of emboli during lesion crossing, the device should be carefully manipulated and not advanced against resistance.
During stent placement, 1.5 cm of vessel should be left between the distal margin of the stent and the Filtration Element. The stent delivery system should not contact the Filtration Element.
Venous access should be available during carotid stenting in order to manage bradycardia and / or hypotension by either pharmaceutical intervention or placement of a temporary pacemaker, if needed.
The device must only be flushed using the 3-ml syringe and flushing tip provided.
The outside diameter of the Outer Sheath is 5.7 Fr. An appropriate sized sheath / guiding catheter should be selected based on this diameter.
Do not use a prepared XACT™ Carotid Stent System if the stent is not fully constrained within the Delivery System.
Do not use if the stent is partially deployed.
If, after preparation, a gap between the catheter tip and the outer sheath exists, rotate the Deployment Actuator in an anti-clockwise direction until the gap is closed.
Advancement and deployment of the XACT™ Carotid Stent System should only be performed under fluoroscopic observation.
Do not advance any component, or section thereof, of the XACT™ Carotid Stent System against significant resistance. The cause of any resistance should be determined via fluoroscopy and remedial action taken.
Do not attempt to reposition the Delivery System once the stent has made contact with the vessel wall.
Do not torque the XACT™ Carotid Stent System.
If more than one stent is required to cover the lesion, or if there are multiple lesions, the distal lesion should be stented first, followed by stenting of the proximal lesion.
If overlap of sequential stents is necessary, the amount of overlap should be kept to a minimum.
Non-clinical testing has demonstrated that the XACT™ Carotid Stent is MR Conditional. It can be scanned safely under the conditions listed in the Instructions for Use.
As reported in the literature, the following adverse events are potentially associated with carotid stents and embolic protection systems:
MAT-2006273 v3.0
STAY CONNECTED